mybatis入门案例自定义实现
一、需要实现的类和接口
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//1.读取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
//3.使用工厂生产SqlSession对象
SqlSession session = factory.openSession();
//4.使用SqlSession创建Dao的代理对象
IUserDao userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//5.使用代理对象执行方法
List<User> users = userDao.findAll();
for(User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//6.释放资源
session.close();
in.close();
}
根据测试类MybatisTest中的main函数,需要实现的类有:Resources、SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,需要实现的接口有:SqlSessionFactory、SqlSession。由于是自定义mybatis,我们将项目配置文件pom.xml中的mybatis的相关信息删除。
二、依据测试类创建缺少的接口和类
1.创建Resources类
在src/main/java目录下,创建mybatis包,在mybatis包下创建io包,在io包下新建类Resources,添加静态方法
//使用类加载器读取配置文件的类
public class Resources {
/**
* @description 根据传入的参数获取一个字节输入流
* @param filePath
* @return
*/
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String filePath){
return Resources.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(filePath);
}
}
之所以这样子添加,我们可以查看原mybatis中,getResourcesAsStream()方法的调用层级,可以发现最终调用的就是ClassLoader类下的getResourceAsStream()方法,因此我们直接调用该方法即可。
//MybatisTest.class
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml");
//Resources.class
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource) throws IOException {
return getResourceAsStream((ClassLoader)null, resource);
}
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader loader, String resource) throws IOException {
InputStream in = classLoaderWrapper.getResourceAsStream(resource, loader);
if (in == null) {
throw new IOException("Could not find resource " + resource);
} else {
return in;
}
}
//ClassLoaderWrapper.class
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return this.getResourceAsStream(resource, this.getClassLoaders(classLoader));
}
InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
ClassLoader[] var3 = classLoader;
int var4 = classLoader.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
ClassLoader cl = var3[var5];
if (null != cl) {
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
if (null == returnValue) {
returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream("/" + resource);
}
if (null != returnValue) {
return returnValue;
}
}
}
return null;
}
//ClassLoader.class
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
Objects.requireNonNull(name);
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
return url != null ? url.openStream() : null;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
2.创建SqlSessionFactorty接口
在mybatis包下新建包sqlsession,在sqlsession包下新建接口SqlSessionFactorty,依据main()方法,该接口中需要声明方法openSession()。
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
//用于打开一个新的SqlSession对象
SqlSession openSession();
}
3.创建SqlSession接口
在sqlsession包下新建接口SqlSessionFactorty,依据main()方法,该接口中需要声明方法getMapper()和close()。
//自定义mybatis中和数据库交互的核心类,可以创建dao接口的代理对象
public interface SqlSession {
/**
* @description 根据参数创建一个代理对象
* @param daoInterfaceClass dao的接口字节码
* @param <T>
* @return
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> daoInterfaceClass);
//释放资源
void close();
}
至于getMapper的声明为什么是这样子,可以查看我的上一篇博客:mybatis入门案例分析
4.创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
在sqlsession包下创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类,添加一个build()方法,先返回空值,之后我们再来补全。
/* 用于创建一个SqlSessionFactory对象 */
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
/**
* @Description: 根据字节输入流来构建一个SqlSessionFactory工厂
* @param config
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream config){
return null;
}
}
在原mybatis中,build()方法调用层级为:
//MybatisTest.class
SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in);
//SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.class
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return this.build((InputStream)inputStream, (String)null, (Properties)null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
SqlSessionFactory var5;
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception var14) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException var13) {
}
}
return var5;
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
可以看到最后返回的是一个DefualtSqlSessionFactory对象,所以在自定义mybatis时,我们也需要返回一个DefuaultSqlSessionFactory对象。而且还用到了xml文件解析类XMLConfigBuilder,因此接下来我们需要定义xml解析类和DefuaultSqlSessionFactory类。
5.创建xml解析类XMLConfigBuilder
解析xml文件,我们采用的是dom4j技术,在查找信息时,用到了XPath。所以我们需要在项目文件pom.xml中添加上相关内容,导入jaxen是为了能够使用XPath:
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
在mybatis包下新建包utils,在utils包下新建类XMLConfigBuilder。解析xml不是本文重点,所以解析类的代码在这里直接给出:
/**
* 用于解析配置文件
*/
public class XMLConfigBuilder {
/**
* 解析主配置文件,把里面的内容填充到DefaultSqlSession所需要的地方
* 使用的技术:dom4j+xpath
*/
public static Configuration loadConfiguration(InputStream config){
try{
//定义封装连接信息的配置对象(mybatis的配置对象)
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
//1.获取SAXReader对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
//2.根据字节输入流获取Document对象
Document document = reader.read(config);
//3.获取根节点
Element root = document.getRootElement();
//4.使用xpath中选择指定节点的方式,获取所有property节点
List<Element> propertyElements = root.selectNodes("//property");
//5.遍历节点
for(Element propertyElement : propertyElements){
//判断节点是连接数据库的哪部分信息
//取出name属性的值
String name = propertyElement.attributeValue("name");
if("driver".equals(name)){
//表示驱动
//获取property标签value属性的值
String driver = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setDriver(driver);
}
if("url".equals(name)){
//表示连接字符串
//获取property标签value属性的值
String url = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setUrl(url);
}
if("username".equals(name)){
//表示用户名
//获取property标签value属性的值
String username = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setUsername(username);
}
if("password".equals(name)){
//表示密码
//获取property标签value属性的值
String password = propertyElement.attributeValue("value");
cfg.setPassword(password);
}
}
//取出mappers中的所有mapper标签,判断他们使用了resource还是class属性
List<Element> mapperElements = root.selectNodes("//mappers/mapper");
//遍历集合
for(Element mapperElement : mapperElements){
//判断mapperElement使用的是哪个属性
Attribute attribute = mapperElement.attribute("resource");
if(attribute != null){
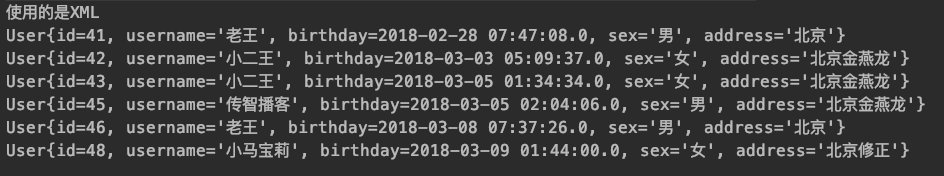
System.out.println("使用的是XML");
//表示有resource属性,用的是XML
//取出属性的值
String mapperPath = attribute.getValue();//获取属性的值"dao/IUserDao.xml"
//把映射配置文件的内容获取出来,封装成一个map
Map<String,Mapper> mappers = loadMapperConfiguration(mapperPath);
//给configuration中的mappers赋值
cfg.setMappers(mappers);
}
}
//返回Configuration
return cfg;
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
try {
config.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 根据传入的参数,解析XML,并且封装到Map中
* @param mapperPath 映射配置文件的位置
* @return map中包含了获取的唯一标识(key是由dao的全限定类名和方法名组成)
* 以及执行所需的必要信息(value是一个Mapper对象,里面存放的是执行的SQL语句和要封装的实体类全限定类名)
*/
private static Map<String,Mapper> loadMapperConfiguration(String mapperPath)throws IOException {
InputStream in = null;
try{
//定义返回值对象
Map<String,Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String,Mapper>();
//1.根据路径获取字节输入流
in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(mapperPath);
//2.根据字节输入流获取Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(in);
//3.获取根节点
Element root = document.getRootElement();
//4.获取根节点的namespace属性取值
String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");//是组成map中key的部分
//5.获取所有的select节点
List<Element> selectElements = root.selectNodes("//select");
//6.遍历select节点集合
for(Element selectElement : selectElements){
//取出id属性的值 组成map中key的部分
String id = selectElement.attributeValue("id");
//取出resultType属性的值 组成map中value的部分
String resultType = selectElement.attributeValue("resultType");
//取出文本内容 组成map中value的部分
String queryString = selectElement.getText();
//创建Key
String key = namespace+"."+id;
//创建Value
Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
mapper.setQueryString(queryString);
mapper.setResultType(resultType);
//把key和value存入mappers中
mappers.put(key,mapper);
}
return mappers;
}catch(Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
in.close();
}
}
}
6.创建配置类Configuration
解析xml文件啊返回的包含有数据库的连接信息、SQL语句和查询结果的封装信息。在mybatis包下创建包config,在config包下新建类Configuration。结合我们之前的入门案例分析,这个类中的属性应该包括:driver,url,username,password,映射信息mappers。
/* 自定义mybatis的配置类 */
public class Configuration {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private Map<String,Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<>();
public Map<String, Mapper> getMappers() {
return mappers;
}
public void setMappers(Map<String, Mapper> mappers) {
this.mappers.putAll(mappers);
}
public String getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
注意:映射信息我们是存放在一个HashMap中,这样可以更加方便地通过完整的id找到SQL语句和查询结果的封装信息。因此接下来我们要定义一个Mapper类,并且setMapper()方法实际上是一个添加新元素并且去重的方法,所以我们不是直接赋值,而是调用putAll()方法。
7.创建Mapper类
结合我们对入门案例的分析,我们知道Mapper类中应该有两大属性,一个是queryString,即我们要执行的SQL语句;另一个是resultType,即封装查询信息的类。在config包下新建类Mapper,如下:
/*用于封装执行的SQL语句和结果类型的全限定类名*/
public class Mapper {
private String queryString;
private String resultType;
public String getQueryString() {
return queryString;
}
public void setQueryString(String queryString) {
this.queryString = queryString;
}
public String getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
public void setResultType(String resultType) {
this.resultType = resultType;
}
}
8.创建SqlSessionFactory接口的实现类DefualtSqlSessionFactory
在mybatis包下新建包defualts,在defualts包下创建类DefualtSqlSessionFactory,openSession()方法返回的是一个操作数据库的对象,要想操作数据库,我们需要提供数据库的连接信息,因此需要添加Configuration类型的字段。
public class DefualtSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration cfg;
public DefualtSqlSessionFactory(Configuration cfg){
this.cfg = cfg;
}
/* 用于创建一个新的操作数据库对象*/
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefualtSqlSession(cfg);
}
}
9.创建SqlSession接口的实现类DefualtSqlSession
在defualts包下创建类DefualtSqlSession。在该类中,我们同样需要配置信息,因此需要添加Configuration类型的字段。为了连接数据库,我们需要添加Connection类型的字段。结合上篇文章的分析,在创建代理对象时,我们需要指定代理方式。接下来我们要实现的就是连接数据库的类DataSourceUtil和调用selectList()方法的InvocationHandler接口的实现类。
public class DefualtSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration cfg;
private Connection connection;
public DefualtSqlSession(Configuration cfg){
this.cfg = cfg;
connection = DataSourceUtil.getConnection(cfg);
}
/* 用于创建代理对象*/
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> daoInterfaceClass) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(daoInterfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{daoInterfaceClass}, new MapperProxy(cfg.getMappers(), connection));
}
/*Description: 用于释放资源*/
@Override
public void close(){
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
10.创建连接数据库的类DataSourceUtil
在utils包下新建类DataSourceUtil:
/* 创建数据源的工具类 */
public class DataSourceUtil {
/* 用于获取一个连接 */
public static Connection getConnection(Configuration cfg){
try {
Class.forName(cfg.getDriver());
return DriverManager.getConnection(cfg.getUrl(),cfg.getUsername(),cfg.getPassword());
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
11.创建InvocationHandler接口的实现类MapperProxy
在mybatis包下新建包proxy,在proxy包下新建类MapperProxy,该类中要对数据库进行查询,所以需要映射信息和数据库连接。在执行查询操作时,我们调用了Executor().selectList(mapper,conn)静态方法,所以接下来我们要定义工具类Executor。
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Map<String, Mapper> mappers;
private Connection conn;
public MapperProxy(Map<String,Mapper> mappers, Connection conn){
this.mappers = mappers;
this.conn = conn;
}
/* 用于对方法进行增强的,其实就是调用selectList方法 */
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//1.获取方法名
String methodName = method.getName();
//2.获取方法所在类的名称
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
//3.组合key
String key = className+"."+methodName;
//4.获取mappers中的Mapper对象
Mapper mapper = mappers.get(key);
//5.判断是否有mapper
if(mapper == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("传入的参数有误");
}
//6.调用工具类执行查询所有
return new Executor().selectList(mapper,conn);
}
}
12.创建查询工具类Executor
在utils包下,新建类Executor:
/* 执行查询封装的工具类 */
public class Executor {
public <E> List<E> selectList(Mapper mapper, Connection conn) {
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1.取出mapper中的数据
String queryString = mapper.getQueryString();//select * from user
String resultType = mapper.getResultType();//domain.User
Class domainClass = Class.forName(resultType);
//2.获取PreparedStatement对象
pstm = conn.prepareStatement(queryString);
//3.执行SQL语句,获取结果集
rs = pstm.executeQuery();
//4.封装结果集
List<E> list = new ArrayList<E>();//定义返回值
while(rs.next()) {
//实例化要封装的实体类对象
E obj = (E)domainClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
//取出结果集的元信息:ResultSetMetaData
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//取出总列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
//遍历总列数
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
//获取每列的名称,列名的序号是从1开始的
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i);
//根据得到列名,获取每列的值
Object columnValue = rs.getObject(columnName);
//给obj赋值:使用Java内省机制(借助PropertyDescriptor实现属性的封装)
PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName,domainClass);//要求:实体类的属性和数据库表的列名保持一种
//获取它的写入方法
Method writeMethod = pd.getWriteMethod();
//把获取的列的值,给对象赋值
writeMethod.invoke(obj,columnValue);
}
//把赋好值的对象加入到集合中
list.add(obj);
}
return list;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
release(pstm,rs);
}
}
private void release(PreparedStatement pstm,ResultSet rs){
if(rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(pstm != null){
try {
pstm.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
13.补全SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类的build方法
build()方法是根据字节输入流来构建一个SqlSessionFactory工厂,因此首先要对xml文件进行解析,读取配置文件,然后返回一个DefualtSqlSessionFactory类的实例。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream config){
Configuration cfg = XMLConfigBuilder.loadConfiguration(config);
return new DefualtSqlSessionFactory(cfg);
}
三、项目结果和执行结果
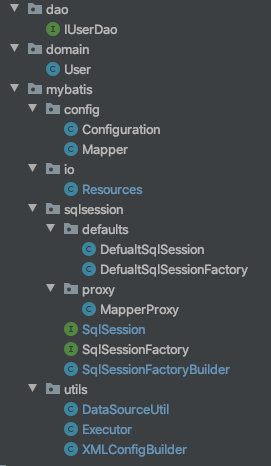
到这里,我们就完成了自定义mybatis的通过xml文件进行配置的实现,之后我们还可以添加提供注解进行配置的实现,项目结构如下;
最后运行测试类的结果为:
四、添加注解的实现
1.修改主配置文件SqlMapConfig
将mapper标签修改为;
<mappers>
<mapper class="dao.IUserDao" />
</mappers>
2.添加注解类
在mybatis包下新建包annocations,在annocations包下新建注解Select,如下:
/* 查询的注解 */
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Select {
//配置SQL语句
String value();
}
3.在dao接口中添加注解
public interface IUserDao {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAll();
}
4.在xml解析类中添加对注解的解析
1、添加通过注解创建映射的函数loadMapperAnnotation()
注意在dao接口中添加注解时,我们并没有添加resultType,因此这里我们获取resultType时运用了反射技术,findAll()方法的返回值是一个List,我们只需找到这个List当中元素的类型即为resultType。
/**
* 根据传入的参数,得到dao中所有被select注解标注的方法。
* 根据方法名称和类名,以及方法上注解value属性的值,组成Mapper的必要信息
* @param daoClassPath
* @return
*/
private static Map<String,Mapper> loadMapperAnnotation(String daoClassPath)throws Exception{
//定义返回值对象
Map<String,Mapper> mappers = new HashMap<String, Mapper>();
//1.得到dao接口的字节码对象
Class daoClass = Class.forName(daoClassPath);
//2.得到dao接口中的方法数组
Method[] methods = daoClass.getMethods();
//3.遍历Method数组
for(Method method : methods){
//取出每一个方法,判断是否有select注解
boolean isAnnotated = method.isAnnotationPresent(Select.class);
if(isAnnotated){
//创建Mapper对象
Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
//取出注解的value属性值
Select selectAnno = method.getAnnotation(Select.class);
String queryString = selectAnno.value();
mapper.setQueryString(queryString);
//获取当前方法的返回值,还要求必须带有泛型信息
Type type = method.getGenericReturnType();//List<User>
//判断type是不是参数化的类型
if(type instanceof ParameterizedType){
//强转
ParameterizedType ptype = (ParameterizedType)type;
//得到参数化类型中的实际类型参数
Type[] types = ptype.getActualTypeArguments();
//取出第一个
Class domainClass = (Class)types[0];
//获取domainClass的类名
String resultType = domainClass.getName();
//给Mapper赋值
mapper.setResultType(resultType);
}
//组装key的信息
//获取方法的名称
String methodName = method.getName();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String key = className+"."+methodName;
//给map赋值
mappers.put(key,mapper);
}
}
return mappers;
}
2、修改loadConfiguration()方法
注解和xml文件进行配置调用的方法是不一样的,这里我们取出mapper标签,判断mapperElement使用的是哪个属性。将第二个循环体修改为:
//取出mappers中的所有mapper标签,判断他们使用了resource还是class属性
List<Element> mapperElements = root.selectNodes("//mappers/mapper");
//遍历集合
for(Element mapperElement : mapperElements){
//判断mapperElement使用的是哪个属性
Attribute attribute = mapperElement.attribute("resource");
if(attribute != null){
System.out.println("使用的是XML");
//表示有resource属性,用的是XML
//取出属性的值
String mapperPath = attribute.getValue();//获取属性的值"dao/IUserDao.xml"
//把映射配置文件的内容获取出来,封装成一个map
Map<String,Mapper> mappers = loadMapperConfiguration(mapperPath);
//给configuration中的mappers赋值
cfg.setMappers(mappers);
}else{
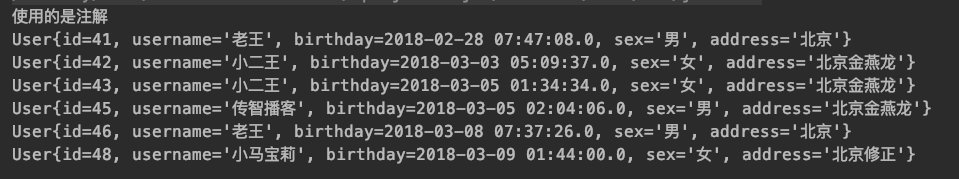
System.out.println("使用的是注解");
//表示没有resource属性,用的是注解
//获取class属性的值
String daoClassPath = mapperElement.attributeValue("class");
//根据daoClassPath获取封装的必要信息
Map<String,Mapper> mappers = loadMapperAnnotation(daoClassPath);
//给configuration中的mappers赋值
cfg.setMappers(mappers);
}
}
5.运行结果
博客链接: