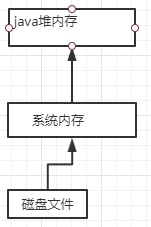
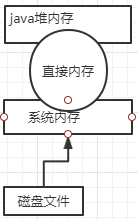
1、定义
(1)常见于NIO操作时,用于数据缓冲区
(2)分配回收成本较高(属于操作系统内存),但读写性能高
(3)不受JVM内存回收管理(依旧存在内存溢出的问题)
2、直接内存基本使用(IO操作举例)
(1)分为两步操作:
(2)使用直接内存后,可以减少步骤:
3、直接内存导致的内存溢出问题
书写程序:每次都分配直接内存,直到内存溢出
public class Test1 {
static int _100Mb=1024*1024*100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<ByteBuffer> list=new ArrayList<>();
int i=0;
try {
while (true){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_100Mb);
list.add(byteBuffer);
i++;
}
}finally {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
测试结果:
17
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Direct buffer memory
at java.nio.Bits.reserveMemory(Bits.java:694)
at java.nio.DirectByteBuffer.<init>(DirectByteBuffer.java:123)
at java.nio.ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(ByteBuffer.java:311)
at pers.zhb.test.Test1.main(Test1.java:15)
4、直接内存的分配与回收(底层通过Unsafe对象管理)
(1)直接内存的分配与回收
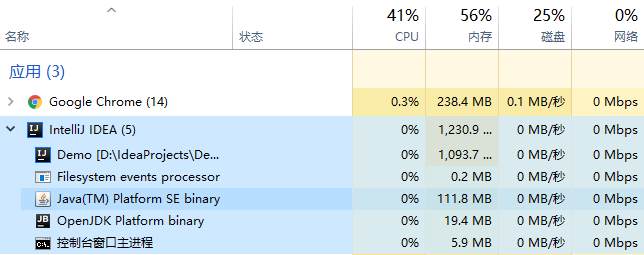
运行程序前:
直接内存的分配与释放程序:
public class Test1 {
static int _1Gb=1024*1024*1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Gb);
System.out.println("分配完毕");
System.in.read();
System.out.println("开始释放");
byteBuffer=null;
System.gc();
}
}
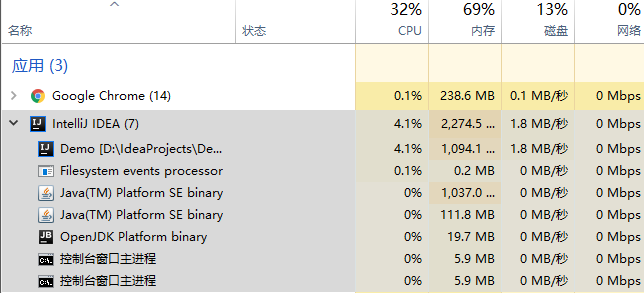
分配直接内存后:
在IDEA的控制台点击回车对内存进行释放:
控制台打印出分配与回收的提示:
分配完毕
开始释放
Process finished with exit code 0
其中System.gc() 回收掉byteBuffer对象
(2)Unsafe实现对直接内存的分配与回收:
public class Test1 {
static int _1Gb=1024*1024*1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Unsafe unsafe=getUnsafe();
//分配内存
long base=unsafe.allocateMemory(_1Gb);
unsafe.setMemory(base,_1Gb,(byte)0);
System.in.read();
//释放内存
unsafe.freeMemory(base);
System.in.read();
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe(){
Field field= null;
try {
field = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
field.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe= null;
try {
unsafe = (Unsafe)field.get(null);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return unsafe;
}
}
jvm的内存分配与回收是自动的,不需要手动调用任何的方法,但是直接内存需要我们手动调用方法
5、ByteBuffer源码
(1)ByteBuffer :
ByteBuffer byteBuffer= ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Gb);
(2)allocateDirect:
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
(3)DirectByteBuffer
DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}
底层用到的依旧是unsafe对象