1、万能map
如果我们的实体类或者数据库中的表、字段或参数过多可以使用它
(1)普通的方式添加一个学生的信息:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="pers.zhb.pojo.Student">
insert into student (studentno,sname,sex,phone)
values (#{studentno},#{sname},#{sex},#{phone})
</insert>
配置文件中,参数的名称要严格对应,必须保证形同
(2)使用万能map:
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="map">
insert into student (studentno,sname,sex,phone)
values (#{a1},#{s2},#{d3},#{f4})
</insert>
没有必要保证参数必须相同,可以为了方便使用简便的命名方式。我们操作的是key,只需要向key传递值。
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession= MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("a1",21);
map.put("s2",21);
map.put("d3",21);
map.put("f4",21);
studentMapper.addStudent(map);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
测试的时候传入的参数为map集合,而普通方式下传入的是一个student对象
(3)接口的定义
void insertStudent(Student student);
int addStudent(Map<String,Object> map);
(4)查询:
接口:
Student findStudentById2(Map<String,Object> map);
配置文件:
<select id="findStudentById2" parameterType="map" resultType="pers.zhb.pojo.Student">
select * from student where studentno = #{s1} and classno=#{c1};
</select>
测试类:
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession= MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("s1",201816);
map.put("c1",80501);
Student student=studentMapper.findStudentById2(map);
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
Student{studentno='201816', sname='jiayou', sex='男', birthday='1998-11-11', classno='80501', point='892', phone='19837372534',
email='null', clas=null}
(5)单个参数(基本数据类型)的情况
不难看出,map在处理多个参数的时候比较方便,在处理单个参数(基本数据类型)的时候就不用考虑命名问题了
接口:
Student findStudentById(Integer studentno);
配置文件:
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="pers.zhb.pojo.Student">
select * from student where studentno = #{as}
</select>
测试类:
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test(){
SqlSession sqlSession= MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper=sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student=studentMapper.findStudentById(201816);
System.out.println(student);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
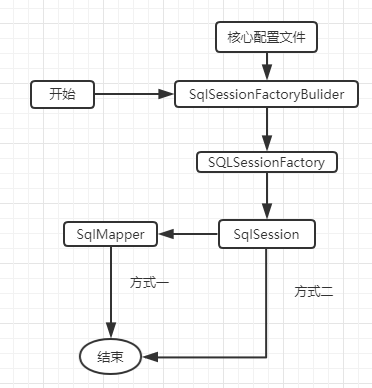
2、生命周期和作用域
生命周期和作用域是至关重要的,因为错误的使用会导致严重的并发问题
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:一旦创建了sqlSessionFactory就不再需要了(局部变量)
SqlSessionFactory:一旦创建就一直存在,相当于一个连接池,最简单的就是使用单例模式或者静态单例模式(应用作用域)
SqlSession:连接到连接池的一个请求,不是线程安全的不能被共享,为了减少资源的占用,用完后需要关闭(请求或方法作用域)