1、注解
注解就是一个类,使用@加上注解名称,开发中可以使用注解取代配置文件
2、@Component 取代
(1)创建一个类(该类与dao层无联系,是一个单独的类)
@Component("studentService")
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
public void addStudent(){
System.out.println("StudentService的实现类的Add方法!!");
}
}
(2)创建配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="pers.zhb.service"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
(3)测试类:
public class TestCycle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
StudentService studentService= (StudentService) applicationContext.getBean("studentService");
studentService.addStudent();
}
}
(4)web开发中,提供了3个@Component注解的衍生注解(功能一样)
@Repository:dao层
@Service:service层
@Controller:web层
3、依赖注入
(1)创建一个Action:
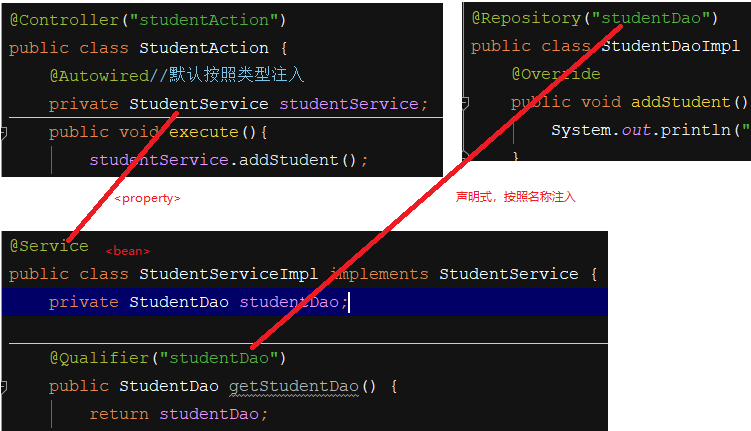
@Controller("studentAction")
public class StudentAction {
@Autowired//默认按照类型注入
private StudentService studentService;
public void execute(){
studentService.addStudent();
}
}
使用@Autowired注解(依赖注入)的时候可以写在属性或set方法处,写在属性处可以节省代码量,优先按照bean的类型去找。
(2)service层:
public interface StudentService {
public void addStudent();
}
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
private StudentDao studentDao;
@Qualifier("studentDao")
public StudentDao getStudentDao() {
return studentDao;
}
@Autowired
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public void addStudent(){
studentDao.addStudent();
}
}
(3)dao层:
public interface StudentDao {
public void addStudent();
}
@Repository("studentDao")
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public void addStudent() {
System.out.println("StudentDao的实现类的Add方法!!");
}
}
(4)配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="pers.zhb"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
(5)测试:
public class ActionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
StudentAction studentAction= (StudentAction) applicationContext.getBean("studentAction");
studentAction.execute();
}
}
StudentDao的实现类的Add方法!!
@Autowired可以省略类内的get和set方法以及配置文件中bean的依赖注入的内容,但是在spring容器中还是需要配置bean的
@service可以省略bean的配置
4、生命周期
初始化:@PostConstruct
销毁:@PreDestory
分别添加到初始化和销毁方法之前。
5、作用域
多例:@Scope(“prototype”)