0 核心类
NettyWebServer
HttpServer
HttpHandler
TcpServer
1 创建 WebServer
根据之前的文章 《Spring Boot启动源码分析》可知,当执行 AbstractApplicationContext -> onRefresh()方法时,如果引入了 webflux 相关依赖,会创建 WebServer。
/** ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext **/
private void createWebServer() {
WebServerManager serverManager = this.serverManager;
if (serverManager == null) {
String webServerFactoryBeanName = getWebServerFactoryBeanName(); // 1.1
ReactiveWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(webServerFactoryBeanName); // 1.1
boolean lazyInit = getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(webServerFactoryBeanName).isLazyInit();
this.serverManager = new WebServerManager(this, webServerFactory, this::getHttpHandler, lazyInit); // 1.2
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.serverManager));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this.serverManager)); // 1.3
}
initPropertySources();
}
1、1、根据 web 容器类型,选择对应的ReactiveWebServerFactory。比如我这里是默认的 Netty,那么webServerFactory就是NettyReactiveWebServerFactory 类型。
1、2、创建WebServerManager对象,用来管理 Server 以及 HttpHandler,入参ReactiveWebServerFactory和HttpHandler都从 bean 容器中获取。
1、3、注册WebServerStartStopLifecycle bean,负责 Server 的启动和停止。
Q:Server 何时启动?
A:
SpringApplication->refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext)方法,调用AbstractApplicationContext->finishRefresh(),之后调用DefaultLifecycleProcessor->onRefresh(),之后调用DefaultLifecycleProcessor->doStart(Map<String, ? extends Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans, String beanName, boolean autoStartupOnly),最终调用 1.3 中的WebServerStartStopLifecycle->start()方法,启动服务。
接下来看下WebServerManager类,
class WebServerManager {
private final ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final DelayedInitializationHttpHandler handler;
private final WebServer webServer;
WebServerManager(ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext applicationContext, ReactiveWebServerFactory factory,
Supplier<HttpHandler> handlerSupplier, boolean lazyInit) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
Assert.notNull(factory, "Factory must not be null");
this.handler = new DelayedInitializationHttpHandler(handlerSupplier, lazyInit);
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(this.handler); // 1.4
}
void start() {
this.handler.initializeHandler();
this.webServer.start(); // 启动 webServer
this.applicationContext
.publishEvent(new ReactiveWebServerInitializedEvent(this.webServer, this.applicationContext));
}
...
}
1、4、创建 webServer,这里会返回NettyWebServer,方法如下:
/** NettyReactiveWebServerFactory **/
public WebServer getWebServer(HttpHandler httpHandler) {
HttpServer httpServer = createHttpServer(); // 1.5
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(httpHandler);
NettyWebServer webServer = new NettyWebServer(httpServer, handlerAdapter, this.lifecycleTimeout, getShutdown());
webServer.setRouteProviders(this.routeProviders);
return webServer;
}
private HttpServer createHttpServer() {
HttpServer server = HttpServer.create(); // 1.6 返回HttpServerBind
if (this.resourceFactory != null) { // 1.7 ReactorResourceFactory是bean
LoopResources resources = this.resourceFactory.getLoopResources();
Assert.notNull(resources, "No LoopResources: is ReactorResourceFactory not initialized yet?");
server = server
.tcpConfiguration((tcpServer) -> tcpServer.runOn(resources).bindAddress(this::getListenAddress)); // 1.8 这里返回HttpServerTcpConfig对象
}
else {
server = server.tcpConfiguration((tcpServer) -> tcpServer.bindAddress(this::getListenAddress));
}
if (getSsl() != null && getSsl().isEnabled()) {
SslServerCustomizer sslServerCustomizer = new SslServerCustomizer(getSsl(), getHttp2(),
getSslStoreProvider());
server = sslServerCustomizer.apply(server);
}
if (getCompression() != null && getCompression().getEnabled()) {
CompressionCustomizer compressionCustomizer = new CompressionCustomizer(getCompression());
server = compressionCustomizer.apply(server);
}
server = server.protocol(listProtocols()).forwarded(this.useForwardHeaders); //1.9 这里返回新的HttpServerTcpConfig对象
return applyCustomizers(server); //1.10 这里返回新的HttpServerTcpConfig对象
}
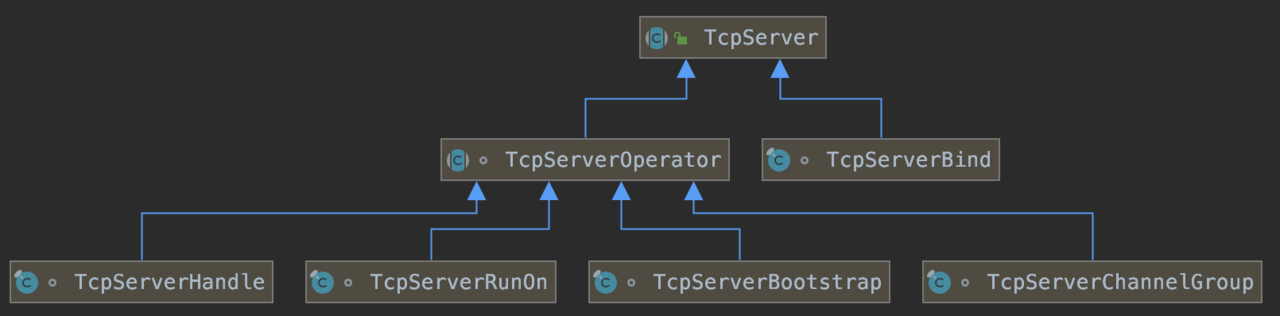
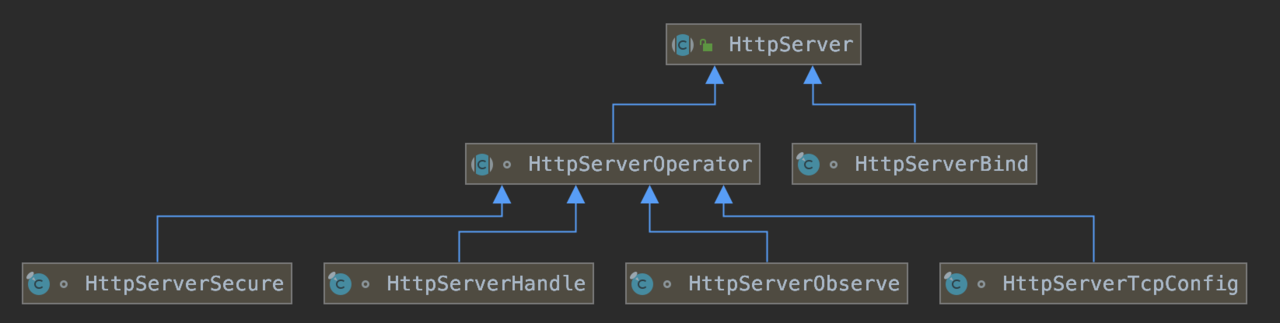
1、5、创建HttpServer,底层是TcpServer,后面分析。
1、7、这里提前创建了NettyReactiveWebServerFactory bean。其中LoopResources负责管理线程,ConnectionProvider负责管理连接。
1、8、 绑定端口;1.9、设置协议类型,比如 Http1.1 还是 Http2;注意这里的入参都是函数,需要等到调用的时候才会执行。
1、10、设置 http 请求头的长度等。
final class HttpServerTcpConfig extends HttpServerOperator {
final Function<? super TcpServer, ? extends TcpServer> tcpServerMapper;
HttpServerTcpConfig(HttpServer server,
Function<? super TcpServer, ? extends TcpServer> tcpServerMapper) {
super(server);
this.tcpServerMapper = Objects.requireNonNull(tcpServerMapper, "tcpServerMapper");
}
@Override
protected TcpServer tcpConfiguration() {
return Objects.requireNonNull(tcpServerMapper.apply(source.tcpConfiguration()),
"tcpServerMapper");
}
}
abstract class HttpServerOperator extends HttpServer {
final HttpServer source;
HttpServerOperator(HttpServer source) {
this.source = Objects.requireNonNull(source, "source");
}
}
1、8、1.9、1.10、返回了大量的新的HttpServerTcpConfig对象,这里 1.5 返回的HttpServer类型应该是HttpServerTcpConfig,并且其 source 也是HttpServerTcpConfig类型,多层嵌套后,最底层的 source 为HttpServerBind类型。
继续看NettyWebServer:
/** NettyWebServer **/
public NettyWebServer(HttpServer httpServer, ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter, Duration lifecycleTimeout,
Shutdown shutdown) {
Assert.notNull(httpServer, "HttpServer must not be null");
Assert.notNull(handlerAdapter, "HandlerAdapter must not be null");
this.lifecycleTimeout = lifecycleTimeout;
this.handler = handlerAdapter;
this.httpServer = httpServer.channelGroup(new DefaultChannelGroup(new DefaultEventExecutor())); // 1.11
this.gracefulShutdown = (shutdown == Shutdown.GRACEFUL) ? new GracefulShutdown(() -> this.disposableServer) : null;
}
1、11、再次返回新的HttpServerTcpConfig,这里创建了线程池EventExecutor。
2 启动 WebServer
/** NettyWebServer **/
private DisposableServer startHttpServer() {
HttpServer server = this.httpServer; // 1.11中的HttpServerTcpConfig对象
if (this.routeProviders.isEmpty()) {
server = server.handle(this.handler); // 2.1 返回HttpServerHandler extends HttpServerOperator
}
else {
server = server.route(this::applyRouteProviders);
}
if (this.lifecycleTimeout != null) {
return server.bindNow(this.lifecycleTimeout);
}
return server.bindNow(); // 2.2
}
/** HttpServer **/
public final HttpServer handle(BiFunction<? super HttpServerRequest, ? super
HttpServerResponse, ? extends Publisher<Void>> handler) {
return new HttpServerHandle(this, handler);
}
/** HttpServerHandler **/
HttpServerHandle(HttpServer server,
BiFunction<? super HttpServerRequest, ? super
HttpServerResponse, ? extends Publisher<Void>> handler) {
super(server);
this.handler = Objects.requireNonNull(handler, "handler");
}
/** HttpServerOperator **/
HttpServerOperator(HttpServer source) {
this.source = Objects.requireNonNull(source, "source"); // 1.11中的HttpServerTcpConfig对象
}
2、1、绑定 handler,此时返回的是HttpServerHandle对象;
2、2、绑定端口并监听。查看源码,发现主要调用了 2 个方法,bind()以及block(timeout)。
/** HttpServer **/
public final DisposableServer bindNow(Duration timeout) {
Objects.requireNonNull(timeout, "timeout");
try {
return Objects.requireNonNull(bind().block(timeout), "aborted");
}
catch (IllegalStateException e) {
if (e.getMessage().contains("blocking read")) {
throw new IllegalStateException("HttpServer couldn't be started within "
+ timeout.toMillis() + "ms");
}
throw e;
}
}
bind()
先看bind()方法:
/** HttpServer **/
public final Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind() {
return bind(tcpConfiguration());
}
protected TcpServer tcpConfiguration() {
return DEFAULT_TCP_SERVER; // 步骤1.6时已经创建
}
static final TcpServer DEFAULT_TCP_SERVER = TcpServer.create();
/** TcpServer **/
public static TcpServer create() {
return TcpServerBind.INSTANCE; // 2.3
}
static final TcpServerBind INSTANCE = new TcpServerBind();
TcpServerBind() {
this.serverBootstrap = createServerBootstrap();
BootstrapHandlers.channelOperationFactory(this.serverBootstrap, TcpUtils.TCP_OPS);
}
ServerBootstrap createServerBootstrap() { // 2.4 残废的ServerBootstrap
return new ServerBootstrap()
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.AUTO_READ, false)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(DEFAULT_PORT));
}
在步骤 1.6 创建HttpServerBind对象时,已经预先创建了TcpServerBind.INSTANCE对象。
按照 OSI 的七层网络模型,端口是在传输层定义的,因此端口的绑定工作,应该有 TCP 层来实现。 所以这里首先是创建了一个TcpServerBind对象,用来负责这个事情。在该类中,有ServerBootstrap属性,可以用来串联 Netty 中的 EventLoopGroup、SocketChannel、Handler。一段典型的 Netty 启动代码如下:
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(boss, worker) // EventLoopGroup
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) // SocketChannel
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)) // ip+port
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { // ChannelHandler
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
...
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.bind().sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully().sync();
worker.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
可以看到,创建的TcpServerBind.INSTANCE中的ServerBootstrap属性缺了很多东西: EventLoopGroup、SocketChannel 以及 Handler。
回头继续看 bind 方法,根据之前的分析,此时的 HttpServer 实际为HttpServerHandler类型,并且其 source 为多次嵌套的HttpServerTcpConfig类型,其最终 source 为HttpServerBind类型。
/** HttpServer **/
public final Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind() {
return bind(tcpConfiguration()); // 2.5 返回的TcpServer是什么类型?
}
/** HttpServerHandler **/
protected TcpServer tcpConfiguration() {
return source.tcpConfiguration().bootstrap(this); // 2.6 返回TcpServerBootstrap
}
/** HttpServerTcpConfig **/
protected TcpServer tcpConfiguration() {
return Objects.requireNonNull(tcpServerMapper.apply(source.tcpConfiguration()),
"tcpServerMapper"); // 2.7 返回TcpServerBootstrap或者TcpServerChannelGroup(1.11步骤)
}
/** HttpServerBind **/
protected TcpServer tcpConfiguration() {
return tcpServer;
}
为了获取步骤 2.5 中的TcpServer,需要先执行HttpServerHandler -> tcpConfiguration(),又需要先多次执行HttpServerTcpConfig -> tcpConfiguration();在步骤 2.7 中,发起了之前函数(步骤1.8,1.9,1.11等)的调用。
结论:步骤 2.5 返回的是TcpServerBootstrap类型,并且其 source 也是TcpServerBootstrap类型(步骤1.11中返回的是TcpServerChannelGroup类型,步骤1.8返回的重点分析),多次嵌套后,其最终 source 为TcpServerBind。
继续往下看:
/** HttpServerBind **/
public Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind(TcpServer delegate) {
return delegate.bootstrap(this) // 返回TcpServerBootstrap
.bind()
.map(CLEANUP_GLOBAL_RESOURCE);
}
/** TcpServer **/
public final TcpServer bootstrap(Function<? super ServerBootstrap, ? extends ServerBootstrap> bootstrapMapper) {
return new TcpServerBootstrap(this, bootstrapMapper);
}
public final Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind() {
ServerBootstrap b;
try{
b = configure(); // 2.8
}
catch (Throwable t){
Exceptions.throwIfJvmFatal(t);
return Mono.error(t);
}
return bind(b); // 2.12
}
/** TcpServerBootstrap **/
public ServerBootstrap configure() {
return Objects.requireNonNull(bootstrapMapper.apply(source.configure()), "bootstrapMapper"); // 2.9
}
/** TcpServerChannelGroup **/
public ServerBootstrap configure() { // 2.10
ServerBootstrap b = source.configure();
b.attr(CHANNEL_GROUP, channelGroup);
ConnectionObserver observer = BootstrapHandlers.childConnectionObserver(b);
BootstrapHandlers.childConnectionObserver(b, observer.then(this));
return b;
}
/** TcpServerBind **/
public ServerBootstrap configure() { // 2.11
return this.serverBootstrap.clone();
}
2、8、链式调用 2.9-2.11 中的configure()方法,主要是给ServerBootstrap配置了一些 childOptions;这里还设置了 group,查看之前 1.8 的源码:发现这里填充了ServerBootstrap的 group 和 channel 属性,只缺少 handler 了。
/** NettyReactiveWebServerFactory **/
server = server
.tcpConfiguration((tcpServer) -> tcpServer.runOn(resources).bindAddress(this::getListenAddress));
/** TcpServer **/
public final TcpServer runOn(LoopResources channelResources) {
return runOn(channelResources, LoopResources.DEFAULT_NATIVE);
}
public final TcpServer runOn(LoopResources channelResources, boolean preferNative) {
return new TcpServerRunOn(this, channelResources, preferNative);
}
/** TcpServerRunOn **/
TcpServerRunOn(TcpServer server, LoopResources loopResources, boolean preferNative) {
super(server);
this.loopResources = Objects.requireNonNull(loopResources, "loopResources");
this.preferNative = preferNative;
}
public ServerBootstrap configure() {
ServerBootstrap b = source.configure();
configure(b, preferNative, loopResources);
return b;
}
static void configure(ServerBootstrap b,
boolean preferNative,
LoopResources resources) {
EventLoopGroup selectorGroup = resources.onServerSelect(preferNative);
EventLoopGroup elg = resources.onServer(preferNative);
b.group(selectorGroup, elg) //熟悉的Netty代码
.channel(resources.onServerChannel(elg));
}
2、9、bootstrapMapper.apply(source.configure()),source.configure()执行完之后,就可以开始执行HttpServer的apply()方法了。
/** HttpServerBind **/
public ServerBootstrap apply(ServerBootstrap b) {
HttpServerConfiguration conf = HttpServerConfiguration.getAndClean(b); // 2.12
SslProvider ssl = SslProvider.findSslSupport(b); // 2.13
if (ssl != null && ssl.getDefaultConfigurationType() == null) {
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h2) == HttpServerConfiguration.h2) {
ssl = SslProvider.updateDefaultConfiguration(ssl,
SslProvider.DefaultConfigurationType.H2);
SslProvider.setBootstrap(b, ssl);
}
else {
ssl = SslProvider.updateDefaultConfiguration(ssl,
SslProvider.DefaultConfigurationType.TCP);
SslProvider.setBootstrap(b, ssl);
}
}
if (b.config()
.group() == null) { // 2.14
LoopResources loops = HttpResources.get();
EventLoopGroup selector = loops.onServerSelect(LoopResources.DEFAULT_NATIVE);
EventLoopGroup elg = loops.onServer(LoopResources.DEFAULT_NATIVE);
b.group(selector, elg)
.channel(loops.onServerChannel(elg));
}
//remove any OPS since we will initialize below
BootstrapHandlers.channelOperationFactory(b);
if (ssl != null) {
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h2c) == HttpServerConfiguration.h2c) { // 2.15
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Configured H2 Clear-Text protocol " +
"with TLS. Use the non clear-text h2 protocol via " +
"HttpServer#protocol or disable TLS" +
" via HttpServer#tcpConfiguration(tcp -> tcp.noSSL())");
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h11orH2) == HttpServerConfiguration.h11orH2) {
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new Http1OrH2Initializer(conf.decoder.maxInitialLineLength(),
conf.decoder.maxHeaderSize(),
conf.decoder.maxChunkSize(),
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.decoder.initialBufferSize(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder,
conf.uriTagValue));
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h11) == HttpServerConfiguration.h11) {
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new Http1Initializer(conf.decoder.maxInitialLineLength(),
conf.decoder.maxHeaderSize(),
conf.decoder.maxChunkSize(),
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.decoder.initialBufferSize(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder,
conf.uriTagValue));
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h2) == HttpServerConfiguration.h2) {
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new H2Initializer(
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder));
}
}
else {
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h2) == HttpServerConfiguration.h2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Configured H2 protocol without TLS. Use" +
" a clear-text h2 protocol via HttpServer#protocol or configure TLS" +
" via HttpServer#secure");
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h11orH2c) == HttpServerConfiguration.h11orH2c) {
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new Http1OrH2CleartextInitializer(conf.decoder.maxInitialLineLength(),
conf.decoder.maxHeaderSize(),
conf.decoder.maxChunkSize(),
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.decoder.initialBufferSize(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder,
conf.uriTagValue,
conf.decoder.h2cMaxContentLength));
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h11) == HttpServerConfiguration.h11) { // 2.16
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new Http1Initializer(conf.decoder.maxInitialLineLength(),
conf.decoder.maxHeaderSize(),
conf.decoder.maxChunkSize(),
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.decoder.initialBufferSize(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder,
conf.uriTagValue));
}
if ((conf.protocols & HttpServerConfiguration.h2c) == HttpServerConfiguration.h2c) {
return BootstrapHandlers.updateConfiguration(b,
NettyPipeline.HttpInitializer,
new H2CleartextInitializer(
conf.decoder.validateHeaders(),
conf.minCompressionSize,
compressPredicate(conf.compressPredicate, conf.minCompressionSize),
conf.forwarded,
conf.cookieEncoder,
conf.cookieDecoder));
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("An unknown HttpServer#protocol " +
"configuration has been provided: "+String.format("0x%x", conf
.protocols));
}
2、12、可以通过ServerBootstrapConfig来获取ServerBootstrap相关的信息,比如childGroup,childHanlder,childOptions,childAttrs。这里把原有 ServerBootstrap 中的attrs -> httpServerConf属性清空了。
2、13、是否支持 ssl,如果支持,需要增加相关的 handler;
2、14、之前已经设置过了;
2、15、如果设置了 ssl,那么就不支持 h2c 协议。http 主要有 3 个协议:h11(http1.1)、h2(http2)、h2c(http2的明文版本);
2、16、根据协议类型,选择合适的 childHandler;比如 http1.1 明文,设置Http1Initializer。
至此,一个完整的ServerBootstrap生成了。接下来就可以进行bind()操作了。
/** TcpServerBind **/
public Mono<? extends DisposableServer> bind(ServerBootstrap b) {
SslProvider ssl = SslProvider.findSslSupport(b);
if (ssl != null && ssl.getDefaultConfigurationType() == null) {
ssl = SslProvider.updateDefaultConfiguration(ssl, SslProvider.DefaultConfigurationType.TCP);
SslProvider.setBootstrap(b, ssl);
}
if (b.config()
.group() == null) {
TcpServerRunOn.configure(b, LoopResources.DEFAULT_NATIVE, TcpResources.get());
}
return Mono.create(sink -> { // 2.17
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = b.clone();
ConnectionObserver obs = BootstrapHandlers.connectionObserver(bootstrap);
ConnectionObserver childObs =
BootstrapHandlers.childConnectionObserver(bootstrap);
ChannelOperations.OnSetup ops =
BootstrapHandlers.channelOperationFactory(bootstrap);
convertLazyLocalAddress(bootstrap);
BootstrapHandlers.finalizeHandler(bootstrap, ops, new ChildObserver(childObs));
ChannelFuture f = bootstrap.bind(); // 正式绑定端口
DisposableBind disposableServer = new DisposableBind(sink, f, obs, bootstrap);
f.addListener(disposableServer);
sink.onCancel(disposableServer);
});
}
2、17、需要注意的是,返回的是 Mono 类型,需要订阅才能触发正式的绑定端口操作。
block()
/** Mono **/
public T block(Duration timeout) {
BlockingMonoSubscriber<T> subscriber = new BlockingMonoSubscriber<>();
subscribe((Subscriber<T>) subscriber);
return subscriber.blockingGet(timeout.toMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
abstract class BlockingSingleSubscriber<T> extends CountDownLatch
implements InnerConsumer<T>, Disposable {
T value;
public final void onSubscribe(Subscription s) {
this.s = s;
if (!cancelled) {
s.request(Long.MAX_VALUE); // 发起请求,触发2.17执行
}
}
3 源码设计思路
- 分层
TcpServer 负责 tcp 协议层的功能,比如绑定端口,比如设置 tcp 层的一些参数
TCP_NODELAY;HttpServer 负责 http 协议的功能,比如编解码。 -
分模块
比如
TcpServerBind负责端口绑定,TcpServerRunOn负责绑定线程池。
同样的,HttpServer 也有类似的设定。
- 链式调用
通过对
TcpServer以及HttpServer的嵌套包装,链式调用其configure()方法或者tcpConfiguration()方法。 - 方法入参为函数,由订阅触发。