1 SpringApplication
SpringApplication 的作用是启动 Spring 应用。一般会做几件事情:
- 创建一个合适的
ApplicationContext; - 注册
CommandLinePropertySource,将程序启动时的命令行参数暴露出来,作为 Spring 的环境变量或者用于 bean 的初始化等; - 刷新
ApplicationContext,加载所有的单例 bean; - 在程序正式运行前执行
CommandLineRunner接口;
/** SpringApplication.java **/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; // 1.1
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); // 1.2
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); // 1.3
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); // 1.4
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); // 1.5
}
1.1 ResourceLoader
资源加载,比如从配置类中加载 classpath:,从文件中加载,从 url 加载等。此处为 null。
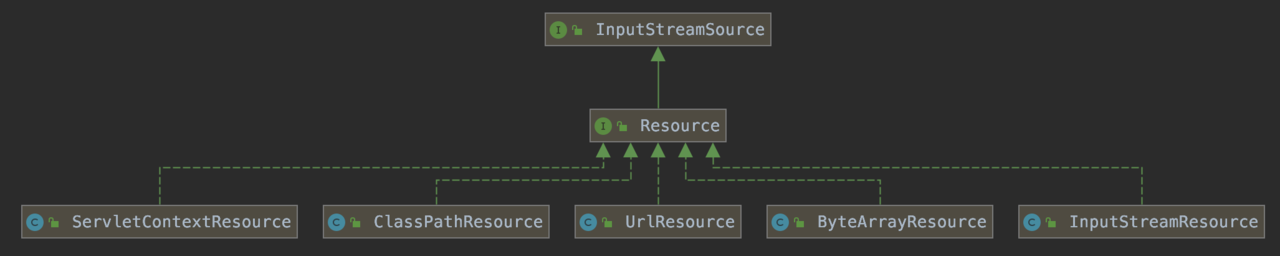
1.2 WebApplicationType
web 类型,有 3 种:NONE、SERVLET、REACTIVE。
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
如果依赖包中存在 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler 类并且不存在 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet,那么就是 REACTIVE 类型。
1.3 ApplicationContextInitializer
初始化 ApplicationContextInitializer 集合。从 jar 包中的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中获取 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer 的值,并通过反射创建实例。
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); // type = ApplicationContextInitializer.class
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
ApplicationContextInitializer 的主要作用就是在 ConfigurableApplicationContext 类型的 ApplicationContext 调用 refresh之前,允许我们对 ConfiurableApplicationContext 的实例做进一步的设置和处理。比如 ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer:设置了一个回调函数,收到事件时将 local.server.port 设置到环境变量中。
public class ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer implements
ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.addApplicationListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
String propertyName = "local." + getName(event.getApplicationContext()) + ".port";
setPortProperty(event.getApplicationContext(), propertyName, event.getWebServer().getPort());
}
}
1.4 ApplicationListener
初始化 ApplicationListener 集合。从 jar 包中的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中获取 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 的值,并通过反射创建实例。
1.5 找到启动类
2 run(String… args)
/** SpringApplication.java **/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 2.1
stopWatch.start(); // 2.1
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // 2.2
listeners.starting(); // 2.2
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); // 2.3
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 2.4
context = createApplicationContext(); // 2.5
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); // 2.6
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 2.7
refreshContext(context); // 2.8
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 2.9
stopWatch.stop(); // 2.1
if (this.logStartupInfo) { // 2.1
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context); // 2.10 发布 `ApplicationStartedEvent` 事件
callRunners(context, applicationArguments); // 2.11
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context); // 2.12 发布 `ApplicationReadyEvent` 事件
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
2.1 StopWatch
用于计时,这里是用来计算程序启动的时间,在日志中会找到类似这样的记录:
Started Application in 1.831 seconds (JVM running for 2.433)
2.2 SpringApplicationRunListener
从 jar 包中的 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中获取 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener 的值,并通过反射创建实例,根据入参 args 创建 ApplicationStartingEvent 事件,并通知给监听者。
看下
EventPublishingRunListener的部分源码:
/** EventPublishingRunListener **/
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { // 1
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args)); // 2
}
}
/** SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster **/
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { // 3
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); // 4
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
3、
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster类获取了所有的ApplicationListener,这样的话当获取到 event 时,就可以通知对应的监听者。4、根据 type 类型,通知对应的监听者,并调用监听者的回调函数。
2.3 ConfigurableEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment(); // 1
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); // 2
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment); // 3
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) { // 1
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
public static void attach(Environment environment) { // 2
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources();
PropertySource<?> attached = sources.get(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
if (attached != null && attached.getSource() != sources) {
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
attached = null;
}
if (attached == null) {
sources.addFirst(new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources))); // 2
}
}
1、创建
StandardEnvironment对象,其中包括MutablePropertySources propertySources字段,用来保存PropertySource列表。这里获取了systemEnvironment以及systemProperties变量。2、这里获取了
configurationProperties相关的变量,并且插入到了MutablePropertySources列表的最前面。3、发布
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,通知监听器回调函数。比如ConfigFileApplicationListener,会把配置文件中的变量加入到applicationConfig。注意:
MutablePropertySources列表里面元素的次序很重要,如果有多个 Source 存在同样的 key,会选择列表中第一个存在该 key 的 Source。比如 ``systemEnvironment的优先级比applicationConfig高,application.yml中配置了server.port=8080,而程序启动时java -jar xxx.jar –server.port=9090`;那么实际监听端口为 9090。看下
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的源码:
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
// 存在多个 PropertySource 时,依次遍历
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
// 一旦找到该 key,直接返回
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
return null;
}
更多信息,参考: 基于SpringBoot的Environment源码理解实现分散配置
2.4 Banner
可自定义,不展开。
2.5 ConfigurableApplicationContext
根据webApplicationType 类型创建 ConfigurableApplicationContext 实例。如果是 REACTIVE 类型,那么创建 AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext实例。
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
看下 AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext构造函数,
public AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
其中 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner都是用来加载注册 bean。
2.6 SpringBootExceptionReporter
创建SpringBootExceptionReporter 实例,用来分析故障并提供诊断信息。查看 FailureAnalyzers 部分源码:
FailureAnalyzers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
this(context, null); // 1
}
FailureAnalyzers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Context must not be null");
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null) ? classLoader : context.getClassLoader();
this.analyzers = loadFailureAnalyzers(this.classLoader); // 2
prepareFailureAnalyzers(this.analyzers, context);
}
private List<FailureAnalyzer> loadFailureAnalyzers(ClassLoader classLoader) {
List<String> analyzerNames = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(FailureAnalyzer.class, classLoader); // 3 从 `META-INF/spring.factories` 从获取 `FailureAnalyzer` 的实现类,`FailureAnalyzer` 可用来分析程序故障并提供诊断信息,比如`NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer`。
List<FailureAnalyzer> analyzers = new ArrayList<>();
for (String analyzerName : analyzerNames) {
try {
Constructor<?> constructor = ClassUtils.forName(analyzerName, classLoader).getDeclaredConstructor();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(constructor);
analyzers.add((FailureAnalyzer) constructor.newInstance()); // 4 创建实例。
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Failed to load %s", analyzerName), ex);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(analyzers);
return analyzers;
}
2.7 prepareContext
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment); // 1 设置环境变量
postProcessApplicationContext(context); // 2
applyInitializers(context); // 3
listeners.contextPrepared(context); // 4
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// 延迟实例化 bean
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); // 5
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); // 5
listeners.contextLoaded(context); // 6
}
3、执行 1.3 实例的
initialize方法。4、发布
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件,通知对应的 listener 处理。5、加载 bean。过程如下: 获取资源(比如配置类、xml、url 等);解析资源为
BeanDefinition;通过BeanDefinitionRegistry的registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)方法进行注册。ApplicationContext中有个Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap,其中 key 为 beanName,value 为BeanDefinition,所谓注册,就是在这个 map 中新增元素,后续可以根据BeanDefinition来创建 bean 实例。
private int load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
return load((Class<?>) source);
}
if (source instanceof Resource) {
return load((Resource) source);
}
if (source instanceof Package) {
return load((Package) source);
}
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
return load((CharSequence) source);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
6、发布
ApplicationPreparedEvent事件,通知对应的 listener 处理。
2.8 refreshContext
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh(); // 1
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 设置 BeanExpressionResolver,ResourceEditorRegistrar 等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 2
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 允许 bean factory 实例化之后进行修改
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 3
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 实例化并调用所有注册的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor Bean
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 4
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册 BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 5
// Initialize message source for this context.
// MessageSource:用于信息的国际化
initMessageSource(); // 6
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化 ApplicationEventMulticaster,用于广播事件
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // 7
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // 8
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 把 listeners 添加到 applicationEventMulticaster(见 step7),用于发布事件;
// 如果当前已有事件(earlyApplicationEvents != null),直接发布
registerListeners(); // 9
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 10
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh(); // 11
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
1、
prepareRefresh():设置当前 Context 为 active 状态,校验必需的环境变量,初始化earlyApplicationListeners和earlyApplicationEvents。
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();
// 可以通过 ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties 设置必需的环境变量;
// 然后在此校验必需的变量是否存在
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
8、
onRefresh():初始化一些特殊的 bean。以ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext为例,创建了ReactiveWebServerFactory,WebServer等对象。
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start reactive web server", ex);
}
}
private void createWebServer() {
ServerManager serverManager = this.serverManager;
if (serverManager == null) {
String webServerFactoryBeanName = getWebServerFactoryBeanName();
ReactiveWebServerFactory webServerFactory = getWebServerFactory(webServerFactoryBeanName);
boolean lazyInit = getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(webServerFactoryBeanName).isLazyInit();
this.serverManager = ServerManager.get(webServerFactory, lazyInit);
}
initPropertySources();
}
2.11 ApplicationRunner & CommandLineRunner
执行 ApplicationRunner & CommandLineRunner 的 run() 方法。
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}