Spring容器初始化 refresh() 方法_02
你的赞,是我最大的动力。期待与大家一起,共同进步。
之前的文章介绍到了,AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()方法,在该方法中有十几个流程,上一篇文章中介绍了refresh()的前四个流程。这篇文章将重点介绍invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)。这个 代码是重点流程,这篇文章详细分析一下。
5.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
5.1 该方法调用流过程
第①步:AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
第②步:PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
2.1 registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry) 处理自定义的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor子类
2.2 DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(java.lang.Class<?>, boolean, boolean) 通过type得到 得到一个Ben的名称
第③步:PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors() spring内部自己实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
第④步:postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry) 不同的子类去自己的实现类中处理,在这里,spring内部的目前为止只有一个实现, 那就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类,该类是spring内置的。
第⑤步:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#processConfigBeanDefinitions(),处理 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
第⑥步:ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate()
第⑦步:ConfigurationClassParser实例化
第⑧步:ConfigurationClassParser#parse(Set)
注:这里的parse()方法及其重要,下一篇文章详细介绍,这里先看一下前面几步涉及的代码逻辑!!!
5.2 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
/**
* getBeanFactoryPostProcessors() 获取自定义的(我们自己实现,且没有交给spring管理的)
*/
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); }
这里自己定义的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现,是指是这个类的子类,但是没有交给spring管理,示例如下:
public class TestFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
int count = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount(); String[] names = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames(); System.out.println("当前BeanFactory中有"+count+" 个Bean"); System.out.println(Arrays.asList(names)); } }
这种方式实现的方式,会通过getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()的方式拿到。
5.2.0 时序图
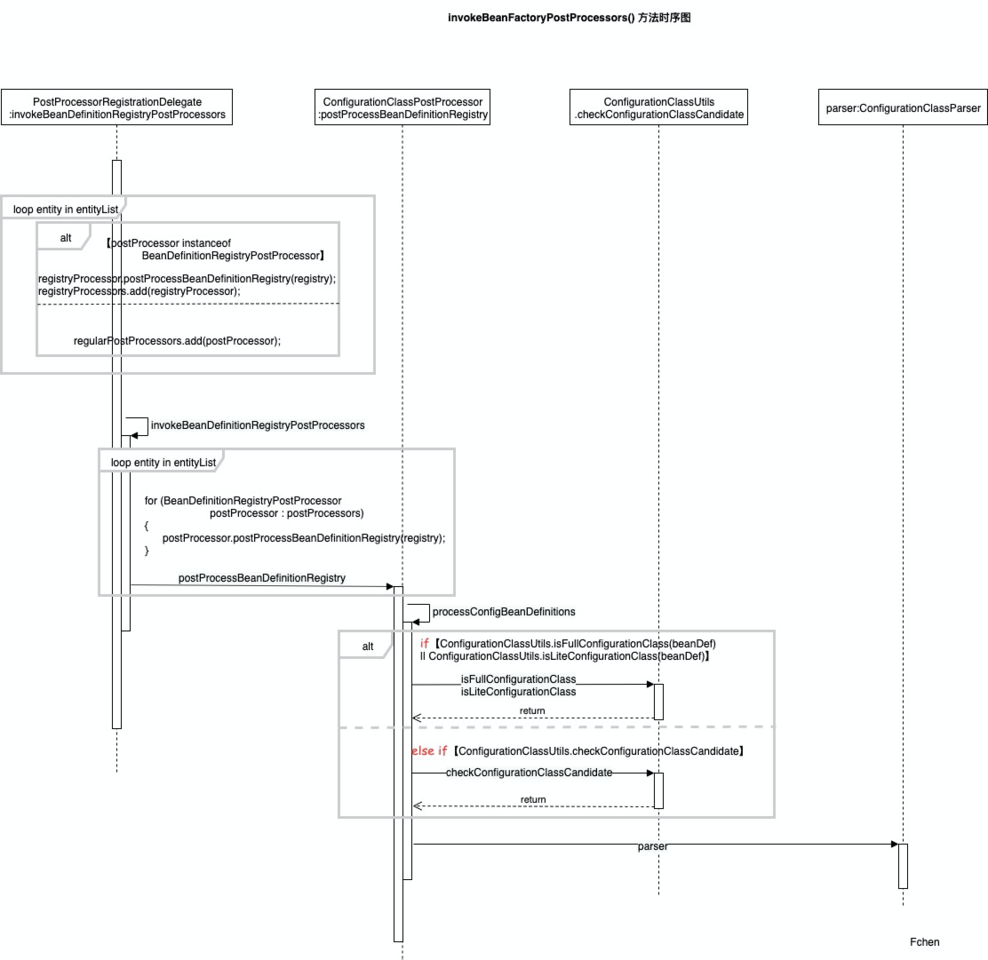
5.2.1 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
/** 对 BeanDefinitionRegistry 类型的处理 */ if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); /** * BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor */ List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); /**自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor*/ for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; /** * 对于 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型, * 在 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的基础上还有自己定义的方法 * 需要先调用 */ registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { /** * 记录常规的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor */ regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } /** * currentRegistryProcessors是放的spring内部自己实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口 */ List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. /** * getBeanNamesForType() 通过type 类型 得到一个Ben的名称、type指的是 spring bean 描述文件的class类型 */ String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); /** * 这个BeanFactory是spring最开始默认注册的 */ for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } /** * 排序 */ sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); /** * 合并list */ registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); /** * spring 中 无论是自己定义的 还是内置的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor * 都在这里处理完成,比如 {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor} 的处理 * 这里是重要代码。。。 */ invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); /** 清除list */ currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } /** * 执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的回调 * 这里执行的是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子类 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的回调方法 * */ invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); /** * 这里执行的是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanFactory() 方法 */ invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
5.2.2 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
/**
* 循环所有的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor */ for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) { /** * 根据不同的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 实现 * 去调用不同的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法 */ postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); } }
通过上述方法,可只在Spring 中先处理程序员自己定义的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,然后在处理Spring中内置的,后者说交给其管理的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,其中 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子类。截止到目前为止 Spring 中唯一的一个内置的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的实现类就是 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 接下来就是对 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的处理。
5.3 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的处理
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
} if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId); /** * 处理 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor */ processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry); }
对 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的真正的处理是通过 processConfigBeanDefinitions 来完成的
5.3.1 processConfigBeanDefinitions
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
/** 存放spring 中 bean的描述文件*/
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
/** 获取容器中所有注册bean的名字*/
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) { /** 根据beanName 获取bean的描述文件 */ BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } /** * 判断是否是Configuration类 是否包含 @Configuration 注解 * checkConfigurationClassCandidate()注意这个方法 */ else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { /** 这里如果添加了 @Configuration * 将该类封装成BeanDefinitionHolder 放入到 configCandidates * 后面解析会用到 */ configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); } } // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; } // Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return Integer.compare(i1, i2); }); // Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null; if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) { BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); if (generator != null) { this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } } if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } // Parse each @Configuration class /** 实例化 ConfigurationClassParser 解析各个配置*/ ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser( this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); /** * 实例化两个Set candidates用于将之前加入的configCandidates 进行去重 * 因为可能有多个配置类重复了 * alreadyParsed 用于判断是否处理过 */ Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size()); do { /** * 解析注解类, * 这里是重点代码 */ parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); // Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content if (this.reader == null) { this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader( registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment, this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } /** * loadBeanDefinitions() 中处理 @Import 的类 */ this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } } while (!candidates.isEmpty()); // Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { // Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op // for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext. ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
5.3.2 对于 beanDef 的判断
对于 beanDef 判断的代码片段如下:
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) ||
ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef);
} }
在 ConfigurationClassUtils 中定义了两个常量用 private static final String CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL = "full" 和 private static final String CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE = "lite" 使用这两个常量用来判断当前的 BeanDefinition 是一个 全配置类还是 部分配置类。在这里对于 @Configuration 注解的配置里走下面的 checkConfigurationClassCandidate 判断,可断点调试验证。
5.3.3 checkConfigurationClassCandidate
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(
BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName();
if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return false; } AnnotationMetadata metadata; if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition && className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) { /** * 如果 beanDefinition 是 AnnotatedBeanDefinition的实例 * 并且 className 和 beanDefinition 中的元数据类名相同 * 从 AnnotatedBeanDefinition 中获取 元数据 */ // Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition... metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata(); } else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) { // Check already loaded Class if present... // since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class. /** * 如果 beanDefinition 是 AbstractBeanDefinition 的实例 * 并且 beanDefinition 有 beanClass属性存在 * 实例化 StandardAnnotationMetadata */ Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass(); metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true); } else { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className); metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); } catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex); } return false; } } /** 判断元数据 是否加了 @Configuration 注解*/ if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { /** * 如果存在 @Configuration 注解,beanDefinition 中设置 configurationClass 为 full * spring 认为该类是一个全注解的类 */ beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL); } /** * 判断是否加了 @Import,@Component * @ImportResource, @ComponentScan 注解 */ else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { /** * 如果不存在 @Configuration 注解,beanDefinition 中设置 configurationClass 为 lite * spring 认为该类是一个部分注解类 */ beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE); } else { return false; } // It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any. Integer order = getOrder(metadata); if (order != null) { beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order); } return true; }
在 checkConfigurationClassCandidate 方法中 @Configuration 注解是的类是 AnnotatedBeanDefinition的实现,首先获取到元数据 metadata 如下图: 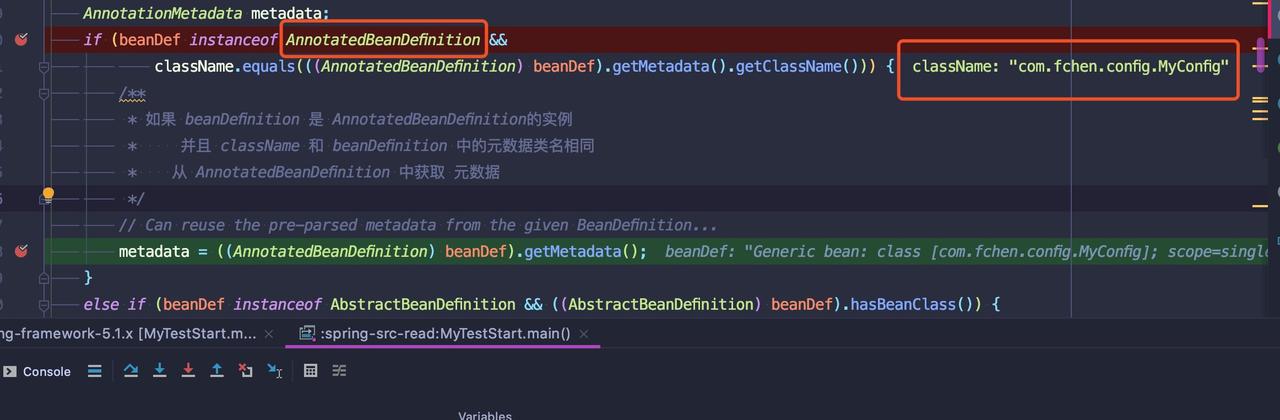
@Configuration注解的类,会将该类的属性设置为 full,如下图: 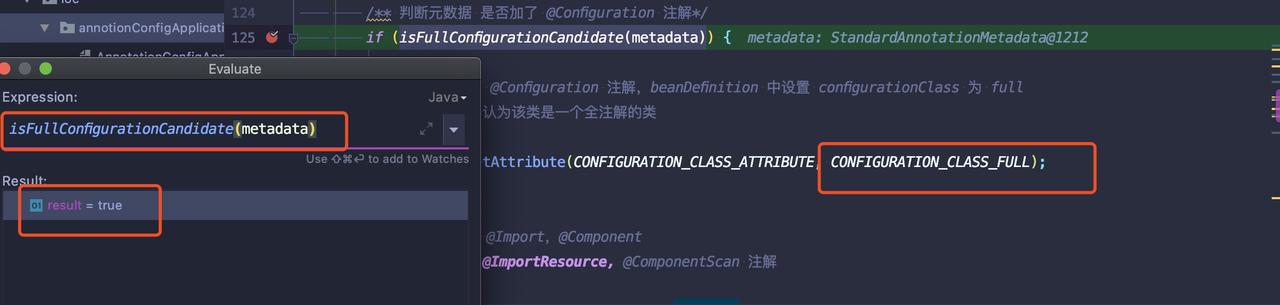
checkConfigurationClassCandidate() 方法返回true,然后将 BeanDefinition 封装成 BeanDefinitionHolder 添加到 configCandidates 中,供后面解析使用。
5.4 ConfigurationClassParser 实例化
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
容器形成图
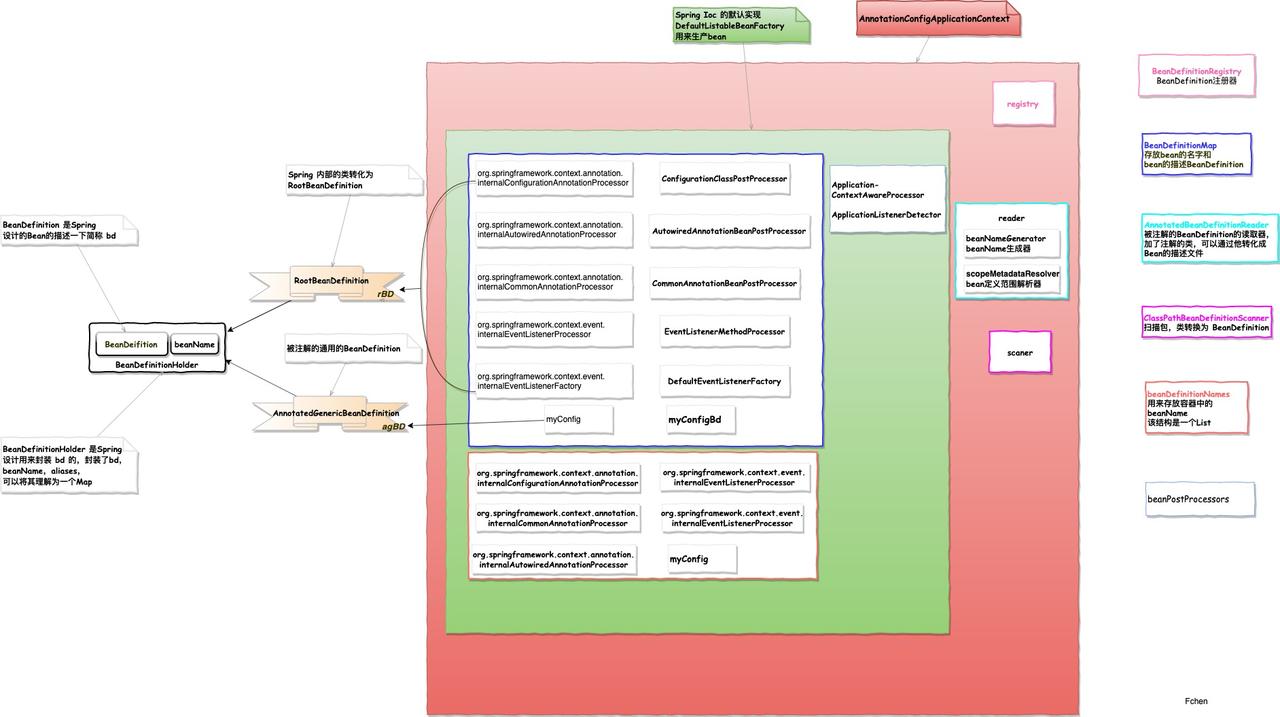
@Configuration注解类对应的Spring内置的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor处理。
本文使用 mdnice 排版