ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,项目中用过xml文件的同学应该会比较熟悉。当我们的项目使用到xml文件来描述 Spring中Bean的时候,我们经常会用到这个容器去获取到相应的Bean。当然目前已经有很多的项目使用的是 注解 和 javaConfig来完成Bean的装配。javaConfig,是在 Spring 3.0 开始从一个独立的项目并入到 Spring 中的。JavaConfig 可以看成一个用于完成 Bean 装配的 Spring 配置文件,即 Spring 容器。这篇文章主要学习一下 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext。
使用
public class ClassPathApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext xmlAppContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-bean.xml");
ClassPathAppContextService service = (ClassPathAppContextService)xmlAppContext.getBean("classPathAppContextService");
service.test();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="classPathAppContextService" class="com.fchen.service.ClassPathAppContextService">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
</beans>
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“spring-bean.xml”)
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
/*
* 调用父类的构造方法
*/
super(parent);
/*
* 设置路径 将配置文件路径 已数组的形式传入
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 中可以对数组进行解析并进行加载
*/
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
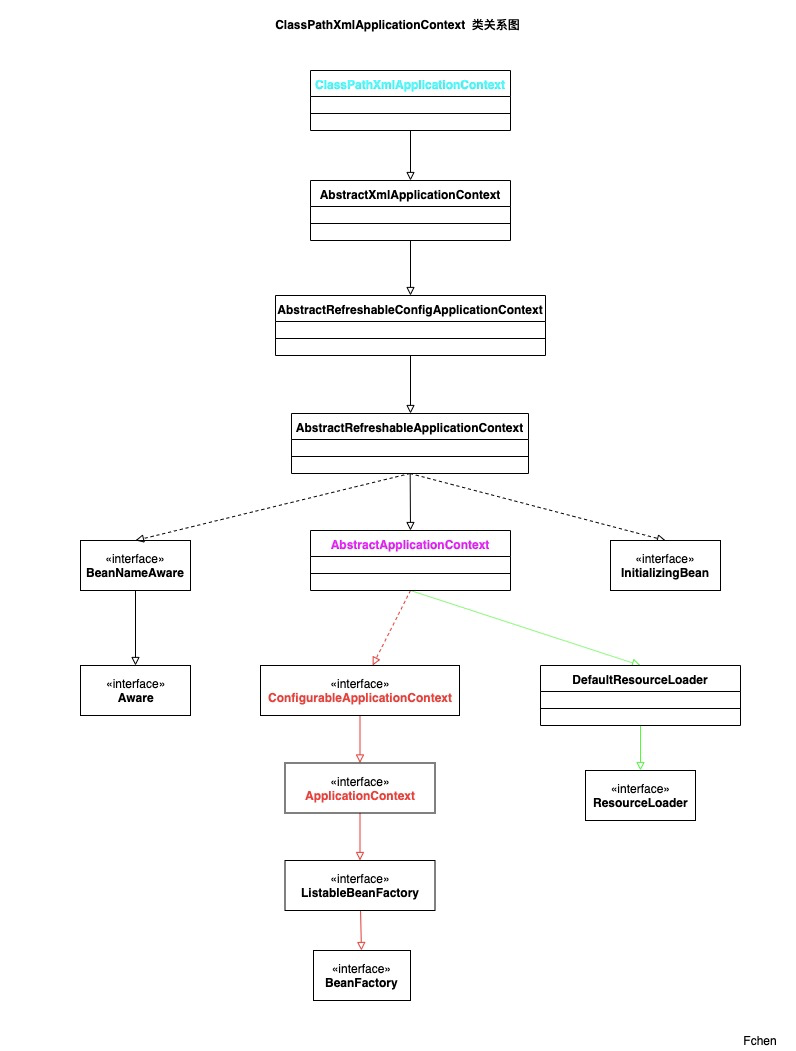
类的继承关系:
从类关系图可以看出,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 在 Spring 的IoC设计中属于BeanFactory -> ListableBeanFactory -> ApplicationContext -> ConfigurableApplicationContext 这一条的设计路线。其中 AbstractApplicationContext 是IOC容器对应具体的实现,并且该类 实现了 DefaultResourceLoader类,这个类主要用于完成资源的加载。通过实现 ResourceLoader接口,使得容器具有了可以将资源文件转化为 Resource 的功能。对于Spring中的资源以及资源加载,在下一篇文章中,统一学习。
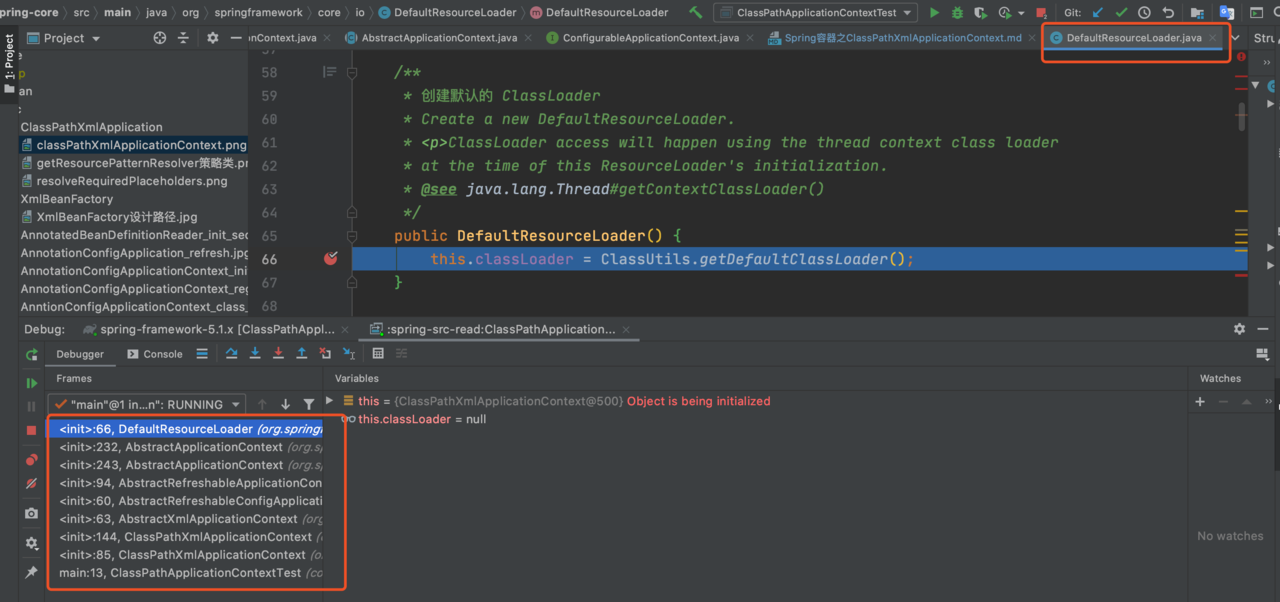
初始化调用过程断点调试截图如下:
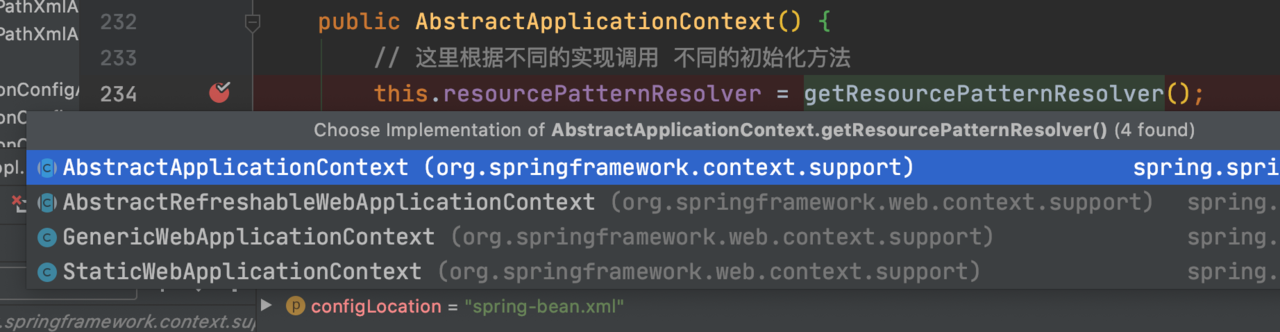
从上图可以看到,都是一层一层的调用父类的方法,最后在 AbstractApplicationContext 的构造方法中通过 this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver(); 来完成 ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver 初始化。这里的 getResourcePatternResolver() 通过不同的策略来完成初始初始化 涉及到的策略类如下图所示:
setConfigLocations(configLocations)
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
// 解析给定路径
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
其中:resolvePath(locations[i]) 的调用流程如下:
①:AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext.resolvePath()
②:AbstractPropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders()
③:AbstractPropertyResolver.doResolvePlaceholders()
④:PropertyPlaceholderHelper.replacePlaceholders(String, PlaceholderResolver)
⑤:PropertyPlaceholderHelper.parseStringValue()
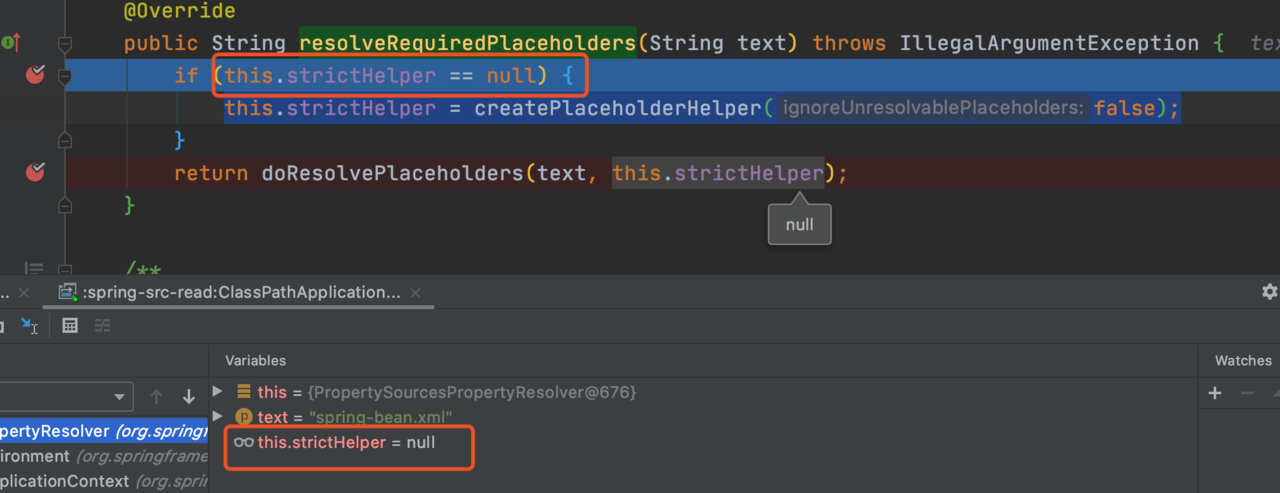
首先看一下 resolveRequiredPlaceholders()方法,的执行,这里会调用 this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
通过 createPlaceholderHelper 完成对 strictHelper 的初始化。
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper createPlaceholderHelper(boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
return new PropertyPlaceholderHelper(this.placeholderPrefix, this.placeholderSuffix,
this.valueSeparator, ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders);
}
从上述流程可以看出最终的调用方法是 parseStringValue() 方法,下面看一下该方法的具体实现:
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, @Nullable Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
// 判断 value 中是否 有 "${"
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
if (startIndex == -1) {
return value;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (visitedPlaceholders == null) {
visitedPlaceholders = new HashSet<>(4);
}
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key
// 如果有占位符,则去掉占位符递归调用本方法,即key=${abc},处理成key=abc的形式试图获取value
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
// 真正的从key-value集合中获得key对应的value
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
// 如果没有找到,则试图按照${key:default}的形式解析
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
// 获得:之前的内容,即真正的key
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
// 获得:之后的内容,即默认值
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
// 再次尝试从key-value集合中获得内容,因为如果真的是key-value的形式,按照全名是肯定找不到的
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
// 如果找到了就按照配置的走,如果没有找到则附上默认值
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
// 如果找到了这个value,则再次递归调用自己,避免value也是占位符的情况
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// 将获得的结果替换掉
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
上述这个方法对通过在xml中使用 ${}方式配置的水泥杆或者@value注解的方式注入field属性完成解析。文中提到的对于xml的解析在第一个 if (startIndex == -1) 处的判断中就返回了。这里先不做详细的分析介绍。
最后在 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 类的无参构造方法中,还有一个极其重要的方法 refresh()。这个方法是 IOC 容器中, 容器初始化最为重要的方法,在该方法中会涉及到BeanDefinition的Resource定位、载入和注册三个过程。这篇文章暂不做介绍,后面会详细学习这个方法中涉及到的功能。
这里注意对比一下 XmlBeanFactory构造方法中的区别,在XmlBeanFactory 的构造方法中初始化了XmlBeanDefinitionReader 对象通过该对象调用loadBeanDefinitions(resource) 完成Bean的定位加载以及注册。而在 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext中,是通过refresh() 来完成的。