1.故事背景
生成一个随机红包,红包的数值0.1元-100元不等,其具体概率为:0.1元为最小单位,0.1元到0.5元的概率为40%,0.5元到1元的概率为50%,1元-2元的概率为5%,2元-3元的概率为3%,3元-4元的概率为1%,4元-5元概率为0.99%,5元-100元的概率为0.01%。
2.思考过程
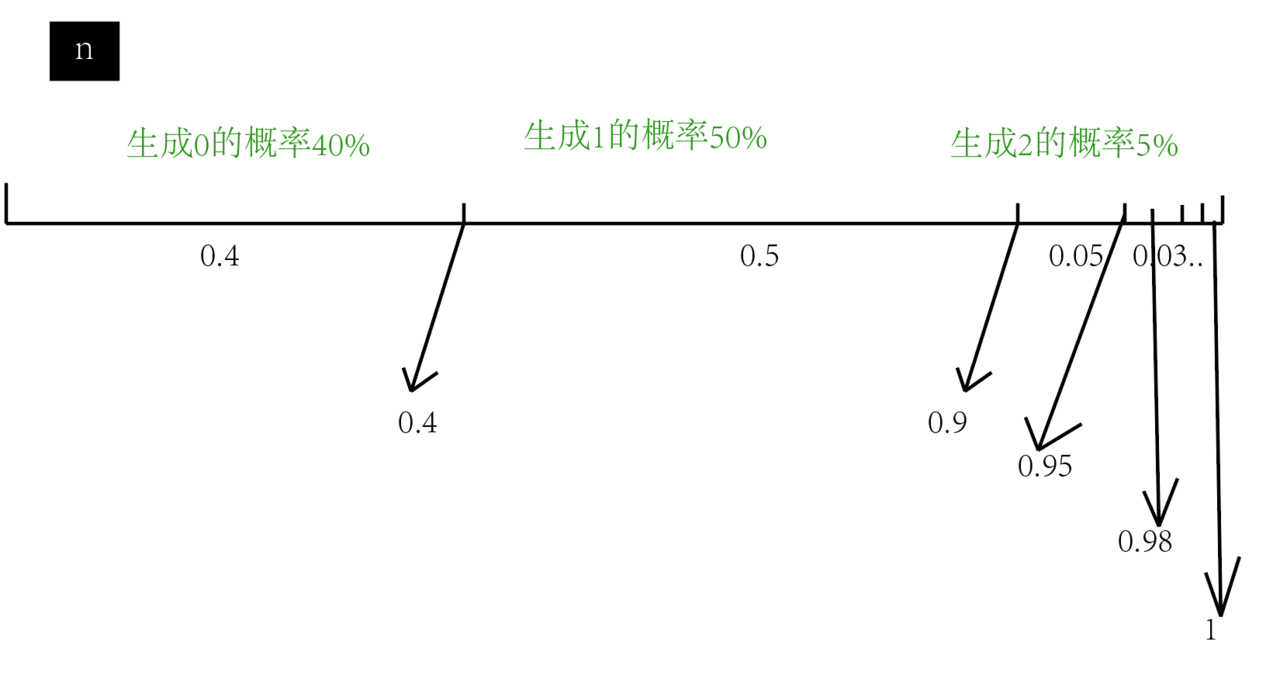
其实问题很简单,把概率放到一条线段上,我们先把问题简单化,假设随机生成0的概率是40%, 生成1的概率是50%,生成2的概率为5%,生成3的概率是3%…,线段上的0.4/0.9/0.95都是计算上两个概率后的和,那么如果我们此时生成一个随机数n,他的随机 的区间是0到1,如果生成0.2,那么就会落到0-0.4的概率区间中,如果是0.7就是 0.4-0.9的概率区间中,符合问题逻辑。
3.实现方式
回到刚开始的故事,就是把第一层的概率逻辑拿过来,然后具体区间中生成的红包数额再进行一次随机数的生成,所以我设计了一个CommonRandom类来存放红包区间的最小值和最大值,还有个该区间的概率,
/**
* @author wangjun
* @Date 2018/3/6
*/
public class CommonRandom {
private Double min;
private Double max;
private Double chance;
private Double calculateRate;
private transient Integer reality = 0;
private transient Double realityRate;
public static CommonRandom getInstance(Double min, Double max, Double rate) {
CommonRandom commonRandom = new CommonRandom();
commonRandom.setMin(min);
commonRandom.setMax(max);
commonRandom.setChance(rate);
return commonRandom;
}
public static String getDefault() {
return JsonUtils.toJson(getCommonRandom());
}
public Double getMin() {
return min;
}
private void setMin(Double min) {
this.min = min;
}
public Double getMax() {
return max;
}
private void setMax(Double max) {
this.max = max;
}
public Double getChance() {
return chance;
}
private void setChance(Double chance) {
this.chance = chance;
}
public Double getCalculateRate() {
return calculateRate;
}
public void setCalculateRate(Double calculateRate) {
this.calculateRate = calculateRate;
}
public Integer getReality() {
return reality;
}
public void setReality(Integer reality) {
this.reality = reality;
}
public Double getRealityRate() {
return realityRate;
}
public void setRealityRate(Double realityRate) {
this.realityRate = realityRate;
}
private static List<CommonRandom> getCommonRandom() {
List<CommonRandom> commonRandomList = Lists.newArrayList();
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(0.1, 0.5, 0.4));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(0.5, 1.0, 0.5));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(1.0, 2.0, 0.05));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(2.0, 3.0, 0.03));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(3.0, 4.0, 0.01));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(4.0, 5.0, 0.0099));
commonRandomList.add(CommonRandom.getInstance(5.0, 100.0, 0.0001));
return commonRandomList;
}
}
生成randomUtil
/**
* @author wangjun
* @Date 2018/3/6
*/
public class RandomUtil {
/**
* 保留小数位数
*/
private static final int POW = (int) Math.pow(10, 3);
private static final double ERROR_RANDOM_RESULT = -1D;
public static Double randomRedPackMoney() {
List<CommonRandom> commonRandoms = CommonRandom.getCommonRandom();
Double result = random(commonRandoms);
if (result == ERROR_RANDOM_RESULT) {
return 1;
}
return result
}
/**
* 返回指定概率生成的随机数
* 传入集合中的chance概率和应为1
* @param commonRandomList 配置生成随机数概率及区间
* @return 随机数
*/
public static Double random(List<CommonRandom> commonRandomList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(commonRandomList)) {
return ERROR_RANDOM_RESULT;
}
double randomNumber = Math.random() * getLastRate(commonRandomList);
for (CommonRandom item : commonRandomList) {
if (randomNumber < item.getCalculateRate()) {
return getRandomNumber(item.getMax(), item.getMin());
}
}
return ERROR_RANDOM_RESULT;
}
private static double getLastRate(List<CommonRandom> commonRandomList) {
return commonRandomList.get(commonRandomList.size() - 1).getCalculateRate();
}
private static Double getRandomNumber(Double max, Double min) {
return Math.floor((Math.random() * (max - min) + min) * POW) / POW;
}
}
以上。