之前的SQL基础1中已经介绍了部分Select的内容,但是,实际使用中select 还有很多其他的用法,本文会再介绍部分select的其他用法。
1. 去重查询
1.1 创建演示表
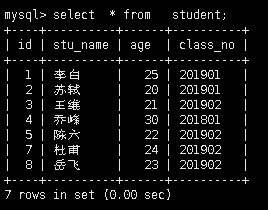
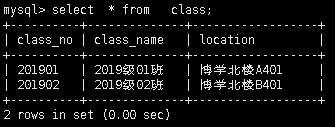
创建2张表用于演示,表名分别为student和class,后续也将继续用这2张表演示,2张表的数据如下:
student表
class表
1.2 查询student表的所有class_no内容
mysql> select class_no from student;
+
| class_no |
+
| 201801 |
| 201901 |
| 201901 |
| 201902 |
| 201902 |
| 201902 |
| 201902 |
+
可见,查询结果中很多重复的情况。
1.3 去重查询所有的class_no
去重使用 DISTINCT 关键字即可
mysql> select distinct class_no from student;
+
| class_no |
+
| 201801 |
| 201901 |
| 201902 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2. 条件查询
条件查询可以有很多种组合,其中用 AND 或 OR连接不同的条件,同时可以用in , not in , >、>=、 <、<=、 =等条件进行范围查询等
2.1 AND条件
AND的意义相当于“且”,也就是AND前后的条件必须同时成立,例如:
查询class_no为201901 并且age>=22的学生
mysql> select * from student where age>=22 and class_no='201901';
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2.2 OR条件
OR意味着“或”,即OR前后条件中的一个满足条件及成立,例如:
查询student表中age>=24 后者班级号为201801的学生
mysql> select * from student where age>=24 or class_no='201801';
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2.3 AND和OR的优先级
AND和OR的优先级顺序是 AND大于OR,有括号的 先处理括号的 。即 AND和OR同时出现时,先处理AND 再与OR判断,但是出现括号,有出现括号的先处理括号里的。例如:
mysql> select * from student where age<23 and class_no='201902' or class_no='201801';
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
建议: 实际使用时,如果嵌套的关系太多,当确定需要先处理哪个关系时建议都加上括号,已避免写法错误导致结果与预期不一致。
2.4 IN或NOT IN
IN 或 NOT IN的使用频率也是非常高的,例如:
mysql> select * from student where class_no in ('201901','201902');
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where class_no not in ('201901','201902');
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3. 排序及分页
3.1 排序
排序使用order by来进行,可以指定一个或多个字段进行排序,同时可以指定升序(ASC,默认的是升序)或降序(DESC)。
mysql> select * from student order by age asc;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student order by age desc;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student order by class_no,age desc;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:当表的数据量较大时,建议排序字段上有索引。
3.2 分页
分页查询在数据展示上是使用频率非常高的功能之一,1其语法为:
select field_names
from tbname
where filter
order by oderby_fieldname
limit offset,row_counts
其中 offset是偏移量,即之前遍历了的数据量,row_counts指每页的数据量。
例如,分页遍历其中一个表的记录,每页3条记录,例如:
mysql> select * from student order by id limit 3*0,3;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student order by id limit 3*1,3;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student order by id limit 3*2,3;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
注: order by 的字段上一定要有索引,否则 可能遍历额结果有重复,相关例子可以自行测试。
4. 聚合查询
很多情况下,我们都需要进行一些汇总类的操作,即聚合查询。聚合查询通常需要配合GROUP BY关键字进行分组聚合。下面使用几种常见的聚合查询操作。
4.1 count
count是指统计记录条数。
4.1.1 不分组的情况下的聚合:
mysql> select count(*) from student;
+
| count(*) |
+
| 7 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from student where age>=24;
+
| count(*) |
+
| 3 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4.1.2 分组情况下聚合:
mysql> select class_no, count(*) from student group by class_no;
+
| class_no | count(*) |
+
| 201801 | 1 |
| 201901 | 2 |
| 201902 | 4 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select class_no, count(*) from student group by class_no order by count(*) desc ;
+
| class_no | count(*) |
+
| 201902 | 4 |
| 201901 | 2 |
| 201801 | 1 |
+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select class_no, count(*) from student group by class_no having count(*)>1 ;
+
| class_no | count(*) |
+
| 201901 | 2 |
| 201902 | 4 |
+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.2 min、max 、avg 、sum
除了count的聚合操作外,还有min(最小)、max(最大) 、avg (平均)、sum(求和)等聚合操作,其操作和count类似。
例如:
mysql> select max(age),min(age),avg(age),sum(age) from student;
+
| max(age) | min(age) | avg(age) | sum(age) |
+
| 30 | 20 | 23.5714 | 165 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5. 子查询
当进行查询下的时候 需要查询的条件是另外一个select语句的结果的时候可以用到子查询来处理。此时要用in、not in 、exists、not exists以及=、!=等。
例如:
mysql> select * from student where class_no in (select class_no from class);
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from student where class_no not in (select class_no from class);
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
exists和not exists在此时(子查询不存在null的情况下)查询结果是等价的(查询效率有差异,且和数据量有关),对于此问题,各位可以自己测一下。
6. 表连接
当需要同时展示多个表的字段时,需要用表连接的方式将多张表的字段在一个查询中展示。
表连接的方式从大类上来说可以分为内连接和外连接。
6.1 内连接
内连接是查询2张表同时存在的记录,即两张表的交集。
例如:
mysql> select * from student a,class b
-> where a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no | class_no | class_name | location |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 | 201901 | 2019级01班 | 博学北楼A401 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 | 201901 | 2019级01班 | 博学北楼A401 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 | 201902 | 2019级02班 | 博学北楼B401 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 | 201902 | 2019级02班 | 博学北楼B401 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 | 201902 | 2019级02班 | 博学北楼B401 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 | 201902 | 2019级02班 | 博学北楼B401 |
+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
注:
a) 例子中是列举出所有字段,所有可以用* ,当需要列出指定字段时,可以列出指定字段名展示,通过表名.字段名的方式列出
b) 内连接的写法可以向上述例子中那样,也可以用inner join … on…这种方式来写,其中inner可以省略,例如:
mysql> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a inner join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| stu_name | class_name |
+
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
c) in可以用内连接的方式来改写,尤其是多层子查询时,这也是SQL优化中给的一种方案。例如之前in例子就可以改写为:
mysql> select distinct a.* from student a inner join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 1 | 李白 | 25 | 201901 |
| 2 | 苏轼 | 20 | 201901 |
| 3 | 王维 | 21 | 201902 |
| 5 | 陈六 | 22 | 201902 |
| 7 | 杜甫 | 24 | 201902 |
| 8 | 岳飞 | 23 | 201902 |
+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6.2 外连接
外连接分为左连接和右连接,其中:
a) 左连接是指包含左边表中的记录,即使左表中含有和右表匹配不上的记录也会保留。
b) 右连接是指包含右边表中的记录,即使右表中含有和左表匹配不上的记录也会保留。
例如:
mysql> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a left join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| stu_name | class_name |
+
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
| 乔峰 | NULL |
+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a right join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| stu_name | class_name |
+
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
+
注: 也可以使用外连接来改写not in ,例如之前not in的例子可以按照如下方式改写:
mysql> select distinct a.* from student a left join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no where b.class_no is null;
+
| id | stu_name | age | class_no |
+
| 4 | 乔峰 | 30 | 201801 |
+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
7. 记录联合
记录联合是指将多个查询结果合并到一起展示,需要用到UNION 、UNION ALL 关键字,其中UNION ALL不对多个查询的结果去重,全部展示出来(即使查询结果完全相同),union 会对结果中的重复记录进行去重后展示。
例如:
mysql> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a left join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no
-> union all
-> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a right join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| stu_name | class_name |
+
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
| 乔峰 | NULL |
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
+
13 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a left join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no
-> union
-> select a.stu_name,b.class_name from student a right join class b on a.class_no=b.class_no;
+
| stu_name | class_name |
+
| 李白 | 2019级01班 |
| 苏轼 | 2019级01班 |
| 王维 | 2019级02班 |
| 陈六 | 2019级02班 |
| 杜甫 | 2019级02班 |
| 岳飞 | 2019级02班 |
| 乔峰 | NULL |
+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)