什么是协程栈
每个协程都需要有自己的栈空间,来存放变量,函数,寄存器等信息。所以系统需要给协程分配足够的栈空间。
栈分配方式
固定大小的栈
每个协程都有相同的,固定大小的栈。
优点:实现简单;
缺点:每个协程需要的栈空间不尽相同,如果一概而论,那么有些是浪费,有些是不够用。
创建时指定
由开发者在创建时指定协程栈大小。java, c++在创建线程时可以指定其栈大小。
优点:实现简单
缺点:对开发者要求比较高,需要根据栈变量,请求量预估。但是有些场景不太好预估,比如递归调用,这种情况通常只能往大的估计。
Segmented stacks
分配和释法额外的内存空间。初始分配的比较小的空间,如4k。不够了再增加,用完即释放。以下是一个例子:
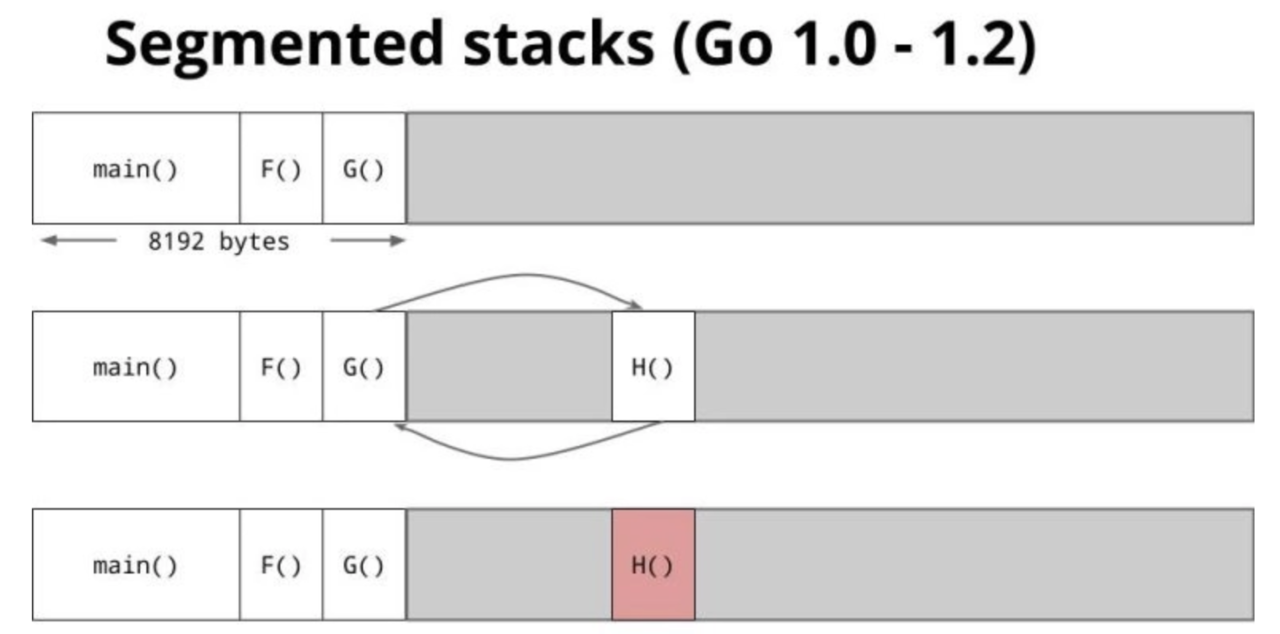
优点:动态扩展,初始成本小,可以将协程当作廉价资源使用。
缺点:存在热分裂问题(hot split problem)。
Stack copying
动态扩展,分配更大的内存,做指针迁移。
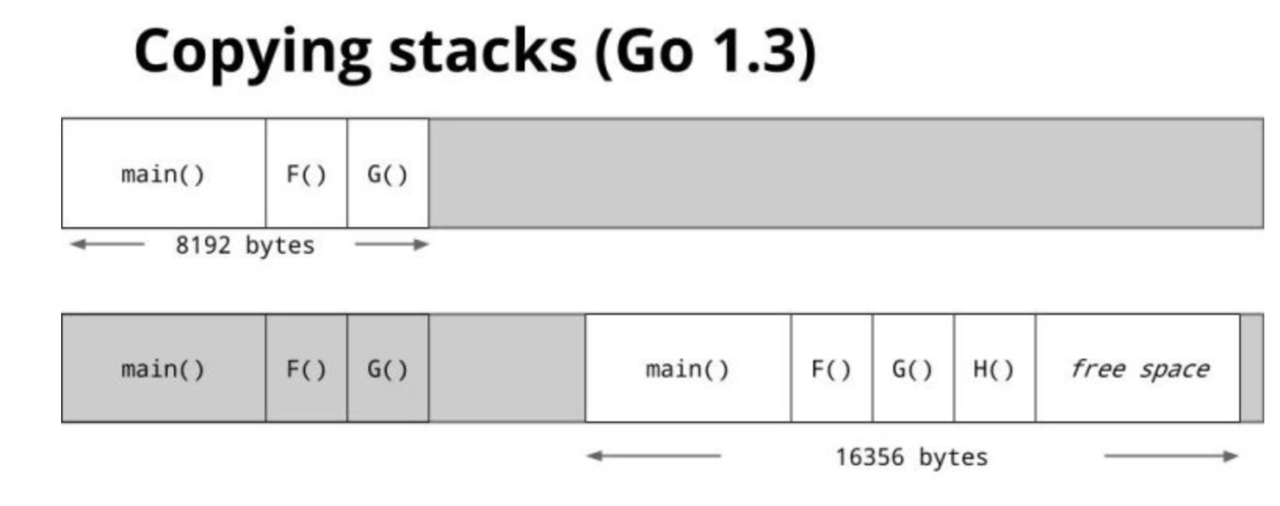
缺点:由于通常以2倍扩展,当请求量密集,内存敏感的情况下,内存会消耗比较多,容易oom,当然,通常的业务量是ok的,不会有任何问题。同时100w连接才要考虑优化。
golang 栈分配方式
1、3之前采用的是Segmented stacks的方式。之后采用的Stack copying,也叫continuous stack(连续栈)
栈扩容
触发时机
运行时,发现栈不够用了
关键步骤
1、 将状态从 _Grunning 更新至 _Gcopystack
2、 计算出需要申请的数据大小
3、 copystack,进行栈复制,后面会详细分析
4、 将协程状态恢复至_Grunning
5、 走一遍协程调度
关键源码
func newstack() {
thisg := getg()
......
gp := thisg.m.curg
......
// Allocate a bigger segment and move the stack.
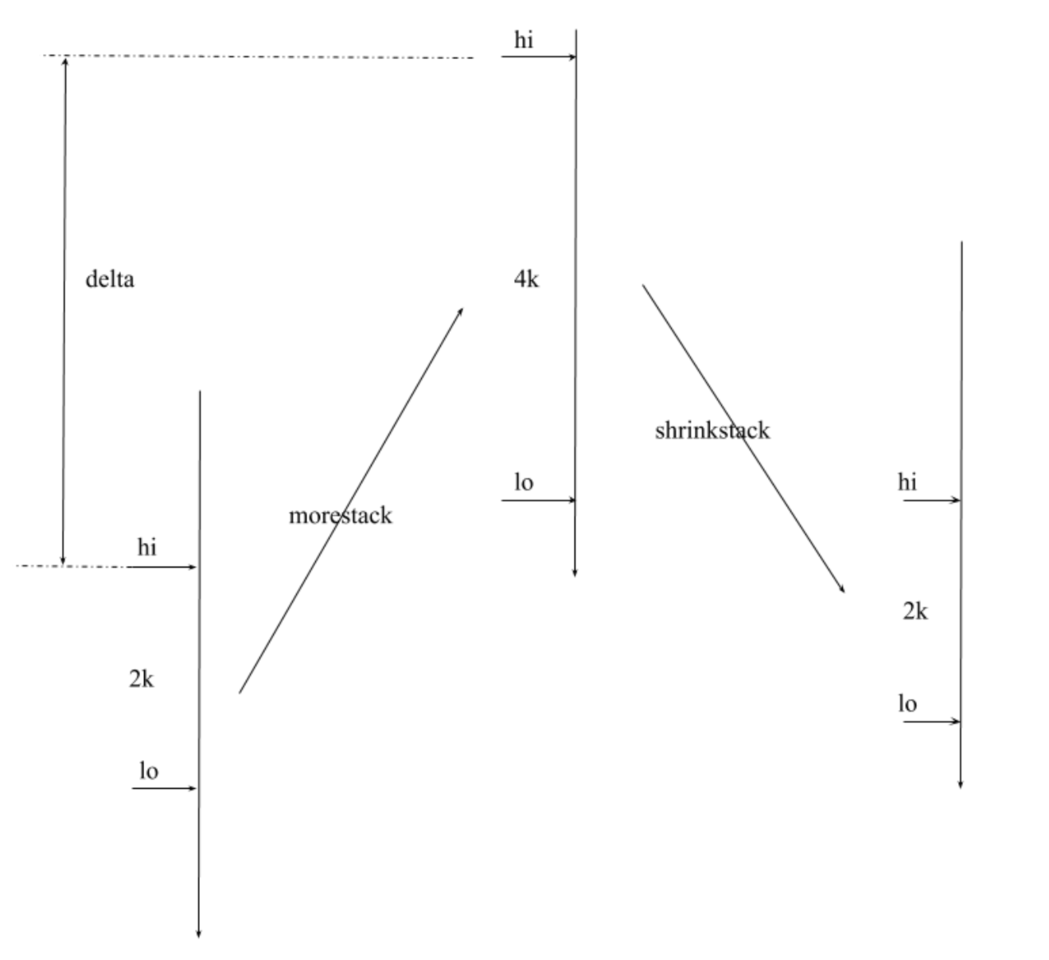
oldsize := gp.stack.hi - gp.stack.lo
newsize := oldsize * 2 // 比原来大一倍
......
// The goroutine must be executing in order to call newstack,
// so it must be Grunning (or Gscanrunning).
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gcopystack) //修改协程状态
// The concurrent GC will not scan the stack while we are doing
// the copy since the gp is in a Gcopystack status.
copystack(gp, newsize, true) //在下面会讲到
......
casgstatus(gp, _Gcopystack, _Grunning)
gogo(&gp.sched)
}
栈缩容
触发时机
gc进行时,非运行中协程,栈使用不超过1/4的,会缩容为原来1/2
关键步骤
1、 检查协程状态,如果已经结束,则释放空间
2、 确定新空间size,目前为原来1/2
3、 检查栈使用是否超过1/4,若没有,则放弃
4、 copystack,进行栈复制,后面会详细分析
关键源码
func shrinkstack(gp *g) {
gstatus := readgstatus(gp)
if gstatus&^_Gscan == _Gdead {
if gp.stack.lo != 0 {
// Free whole stack - it will get reallocated
// if G is used again.
stackfree(gp.stack)
gp.stack.lo = 0
gp.stack.hi = 0
}
return
}
......
oldsize := gp.stack.hi - gp.stack.lo
newsize := oldsize / 2 // 比原来小1倍
if newsize < _FixedStack {
return
}
// Compute how much of the stack is currently in use and only
// shrink the stack if gp is using less than a quarter of its
// current stack. The currently used stack includes everything
// down to the SP plus the stack guard space that ensures
// there's room for nosplit functions.
avail := gp.stack.hi - gp.stack.lo
//当已使用的栈占不到总栈的1/4 进行缩容
if used := gp.stack.hi - gp.sched.sp + _StackLimit; used >= avail/4 {
return
}
copystack(gp, newsize, false) //在下面会讲到
}
copystack栈拷贝过程
原来内容上的拷贝
关键步骤
1、 申请新的栈空间:new := stackalloc(uint32(newsize));
2、 调整指针指向,将sudog,ctx等,指向新位置,计算方式为原地址+delta(delta为new.hi-old.hi);
3、 gentraceback,调整栈帧到新位置;
4、 memmove老栈数据到新栈;
5、 删除老栈。
func copystack(gp *g, newsize uintptr, sync bool) {
......
old := gp.stack
......
used := old.hi - gp.sched.sp
// allocate new stack
new := stackalloc(uint32(newsize))
......
// Compute adjustment.
var adjinfo adjustinfo
adjinfo.old = old
adjinfo.delta = new.hi - old.hi //用于旧栈指针的调整
//后面有机会和 select / chan 一起分析
// Adjust sudogs, synchronizing with channel ops if necessary.
ncopy := used
if sync {
adjustsudogs(gp, &adjinfo)
} else {
......
adjinfo.sghi = findsghi(gp, old)
// Synchronize with channel ops and copy the part of
// the stack they may interact with.
ncopy -= syncadjustsudogs(gp, used, &adjinfo)
}
//把旧栈数据复制到新栈
// Copy the stack (or the rest of it) to the new location
memmove(unsafe.Pointer(new.hi-ncopy), unsafe.Pointer(old.hi-ncopy), ncopy)
// Adjust remaining structures that have pointers into stacks.
// We have to do most of these before we traceback the new
// stack because gentraceback uses them.
adjustctxt(gp, &adjinfo)
adjustdefers(gp, &adjinfo)
adjustpanics(gp, &adjinfo)
......
// Swap out old stack for new one
gp.stack = new
gp.stackguard0 = new.lo + _StackGuard // NOTE: might clobber a preempt request
gp.sched.sp = new.hi - used
gp.stktopsp += adjinfo.delta
// Adjust pointers in the new stack.
gentraceback(^uintptr(0), ^uintptr(0), 0, gp, 0, nil, 0x7fffffff, adjustframe, noescape(unsafe.Pointer(&adjinfo)), 0)
......
//释放旧栈
stackfree(old)
}
栈帧调整
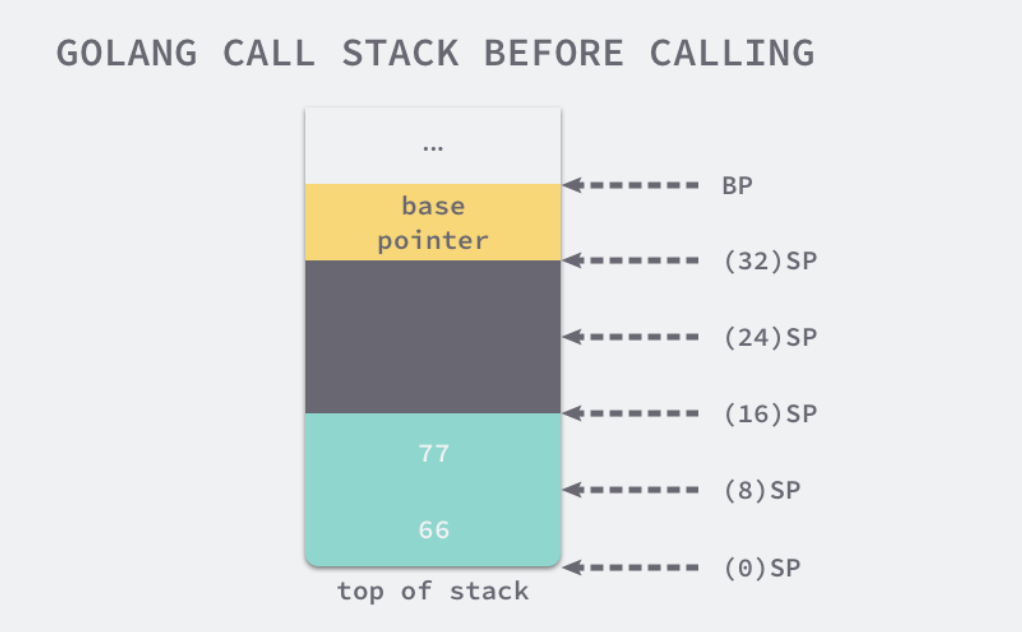
golang栈帧
package main
func myFunction(a, b int) (int, int) {
return a + b, a - b
}
func main() {
myFunction(66, 77)
}
栈帧调整
gentraceback里回调了adjustframe函数,我们所需要了解的即golang的栈空间中,有存放函数参数,返回值,函数返回地址等信息,这些地址都需要调节,该函数就是针对原来的栈指针进行的调节。代码如下:
// Note: the argument/return area is adjusted by the callee.
func adjustframe(frame *stkframe, arg unsafe.Pointer) bool {
adjinfo := (*adjustinfo)(arg)
targetpc := frame.continpc
if targetpc == 0 {
// Frame is dead.
return true
}
f := frame.fn
.........
pcdata := pcdatavalue(f, _PCDATA_StackMapIndex, targetpc, &adjinfo.cache)
if pcdata == -1 {
pcdata = 0 // in prologue
}
// Adjust local variables if stack frame has been allocated.
size := frame.varp - frame.sp
var minsize uintptr
switch sys.ArchFamily {
case sys.ARM64:
minsize = sys.SpAlign
default:
minsize = sys.MinFrameSize
}
if size > minsize {
var bv bitvector
stackmap := (*stackmap)(funcdata(f, _FUNCDATA_LocalsPointerMaps))
if stackmap == nil || stackmap.n <= 0 {
print("runtime: frame ", funcname(f), " untyped locals ", hex(frame.varp-size), "+", hex(size), "\n")
throw("missing stackmap")
}
// Locals bitmap information, scan just the pointers in locals.
if pcdata < 0 || pcdata >= stackmap.n {
print("runtime: pcdata is ", pcdata, " and ", stackmap.n, " locals stack map entries for ", funcname(f), " (targetpc=", targetpc, ")\n")
throw("bad symbol table")
}
bv = stackmapdata(stackmap, pcdata)
size = uintptr(bv.n) * sys.PtrSize
if stackDebug >= 3 {
print(" locals ", pcdata, "/", stackmap.n, " ", size/sys.PtrSize, " words ", bv.bytedata, "\n")
}
adjustpointers(unsafe.Pointer(frame.varp-size), &bv, adjinfo, f)
}
// Adjust saved base pointer if there is one.
if sys.ArchFamily == sys.AMD64 && frame.argp-frame.varp == 2*sys.RegSize {
if !framepointer_enabled {
print("runtime: found space for saved base pointer, but no framepointer experiment\n")
print("argp=", hex(frame.argp), " varp=", hex(frame.varp), "\n")
throw("bad frame layout")
}
if stackDebug >= 3 {
print(" saved bp\n")
}
if debugCheckBP {
// Frame pointers should always point to the next higher frame on
// the Go stack (or be nil, for the top frame on the stack).
bp := *(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(frame.varp))
if bp != 0 && (bp < adjinfo.old.lo || bp >= adjinfo.old.hi) {
println("runtime: found invalid frame pointer")
print("bp=", hex(bp), " min=", hex(adjinfo.old.lo), " max=", hex(adjinfo.old.hi), "\n")
throw("bad frame pointer")
}
}
adjustpointer(adjinfo, unsafe.Pointer(frame.varp))
}
// Adjust arguments.
if frame.arglen > 0 {
var bv bitvector
if frame.argmap != nil {
bv = *frame.argmap
} else {
stackmap := (*stackmap)(funcdata(f, _FUNCDATA_ArgsPointerMaps))
if stackmap == nil || stackmap.n <= 0 {
print("runtime: frame ", funcname(f), " untyped args ", frame.argp, "+", frame.arglen, "\n")
throw("missing stackmap")
}
if pcdata < 0 || pcdata >= stackmap.n {
print("runtime: pcdata is ", pcdata, " and ", stackmap.n, " args stack map entries for ", funcname(f), " (targetpc=", targetpc, ")\n")
throw("bad symbol table")
}
bv = stackmapdata(stackmap, pcdata)
}
if stackDebug >= 3 {
print("args\n")
}
adjustpointers(unsafe.Pointer(frame.argp), &bv, adjinfo, funcInfo{})
}
return true
}