先抛开之前所看到的 Tomcat 源码不谈,Tomcat 作为一个用 Java 实现的 Web 服务器,如果让你来实现,那么从何入手?
这里首先需要厘清的是 Web 服务器的概念,谷歌了一下,发现这条解释还算靠谱点,【在网络环境下可以向发出请求的浏览器提供文档的程序】。重点有两条:1.网络环境下,2.能够给出响应。用 Java 写过网络通信程序的都知道,这里必然会用到 Socket 编程。我们自己要实现的服务器程序作为 Socket 编程里的服务端,浏览器作为 Socket 编程里的客户端。
要理解 Tomcat 原理,Socket 编程这块的基本原理必须得了解,google 一把一大堆,这里不再单独做介绍。下面给出一个服务器端最简单的响应客户端请求的伪代码示例:
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080, 1,
InetAddress.getByName(“localhost”));
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
socket = serverSocket.accept();//1.监听到客户端的连接
is = socket.getInputStream();
os = socket.getOutputStream();
Request request = Util.getRequest(is);//2.从输入流中读取数据,并根据Http协议转换成请求
Response response = Util.service(request);//服务器内部根据请求信息给出响应信息
os.writeResponse(response);//3.将响应信息写到输出流
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {//4.关闭输入输出流及连接
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
socket.close();
}
浏览器和 Web 服务器的一次交互过程分四步:连接、请求、响应、关闭。前一篇文章分析到的接收器线程,如前文开始截图里的 http-bio-8080-Acceptor-0 ,这个线程的实现类org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.Acceptor,源码如下:
1 // --------------------------------------------------- Acceptor Inner Class
2 /**
3 * The background thread that listens for incoming TCP/IP connections and
4 * hands them off to an appropriate processor.
5 */
6 protected class Acceptor extends AbstractEndpoint.Acceptor {
7
8 @Override
9 public void run() {
10
11 int errorDelay = 0;
12
13 // Loop until we receive a shutdown command
14 while (running) {
15
16 // Loop if endpoint is paused
17 while (paused && running) {
18 state = AcceptorState.PAUSED;
19 try {
20 Thread.sleep(50);
21 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
22 // Ignore
23 }
24 }
25
26 if (!running) {
27 break;
28 }
29 state = AcceptorState.RUNNING;
30
31 try {
32 //if we have reached max connections, wait
33 countUpOrAwaitConnection();
34
35 Socket socket = null;
36 try {
37 // Accept the next incoming connection from the server
38 // socket
39 socket = serverSocketFactory.acceptSocket(serverSocket);
40 } catch (IOException ioe) {
41 countDownConnection();
42 // Introduce delay if necessary
43 errorDelay = handleExceptionWithDelay(errorDelay);
44 // re-throw
45 throw ioe;
46 }
47 // Successful accept, reset the error delay
48 errorDelay = 0;
49
50 // Configure the socket
51 if (running && !paused && setSocketOptions(socket)) {
52 // Hand this socket off to an appropriate processor
53 if (!processSocket(socket)) {
54 countDownConnection();
55 // Close socket right away
56 closeSocket(socket);
57 }
58 } else {
59 countDownConnection();
60 // Close socket right away
61 closeSocket(socket);
62 }
63 } catch (IOException x) {
64 if (running) {
65 log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), x);
66 }
67 } catch (NullPointerException npe) {
68 if (running) {
69 log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), npe);
70 }
71 } catch (Throwable t) {
72 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
73 log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.accept.fail"), t);
74 }
75 }
76 state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
77 }
78 }
第 39 行做的事就是上面伪代码示例里的监听客户端连接,监听到连接后(即浏览器向服务器发起一次请求)在第 53 行由 processSocket 方法来处理这次接收到的 Socket 连接。processSocket 方法源码如下:
1 protected boolean processSocket(Socket socket) {
2 // Process the request from this socket
3 try {
4 SocketWrapper<Socket> wrapper = new SocketWrapper<Socket>(socket);
5 wrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
6 // During shutdown, executor may be null - avoid NPE
7 if (!running) {
8 return false;
9 }
10 getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(wrapper));
11 } catch (RejectedExecutionException x) {
12 log.warn("Socket processing request was rejected for:"+socket,x);
13 return false;
14 } catch (Throwable t) {
15 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
16 // This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
17 // the pool and its queue are full
18 log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
19 return false;
20 }
21 return true;
22 }
该方法中先把 Socket 包装成 SocketWrapper ,用以内部处理。重点是第 10 行:getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(wrapper))。如果按照上面伪代码中的处理方式,在有并发请求的情况下,一个请求没有处理完成,服务器将无法立即响应另一个请求。这里做了一下改进,即在接收到一次 Socket 连接后另启一个线程处理该连接,使当前线程不阻塞。
下面跟着 SocketProcessor 这个线程来看看,一次 Socket 连接是如何在 Tomcat 7 中被转成内部的 Request 的。看下该线程的 run 方法:
1 @Override
2 public void run() {
3 boolean launch = false;
4 synchronized (socket) {
5 try {
6 SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
7
8 try {
9 // SSL handshake
10 serverSocketFactory.handshake(socket.getSocket());
11 } catch (Throwable t) {
12 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
13 if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
14 log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.handshake"), t);
15 }
16 // Tell to close the socket
17 state = SocketState.CLOSED;
18 }
19
20 if ((state != SocketState.CLOSED)) {
21 if (status == null) {
22 state = handler.process(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN);
23 } else {
24 state = handler.process(socket,status);
25 }
26 }
27 if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
28 // Close socket
29 if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
30 log.trace("Closing socket:"+socket);
31 }
32 countDownConnection();
33 try {
34 socket.getSocket().close();
35 } catch (IOException e) {
36 // Ignore
37 }
38 } else if (state == SocketState.OPEN ||
39 state == SocketState.UPGRADING ||
40 state == SocketState.UPGRADED){
41 socket.setKeptAlive(true);
42 socket.access();
43 launch = true;
44 } else if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
45 socket.access();
46 waitingRequests.add(socket);
47 }
48 } finally {
49 if (launch) {
50 try {
51 getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN));
52 } catch (RejectedExecutionException x) {
53 log.warn("Socket reprocessing request was rejected for:"+socket,x);
54 try {
55 //unable to handle connection at this time
56 handler.process(socket, SocketStatus.DISCONNECT);
57 } finally {
58 countDownConnection();
59 }
60
61
62 } catch (NullPointerException npe) {
63 if (running) {
64 log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.launch.fail"),
65 npe);
66 }
67 }
68 }
69 }
70 }
71 socket = null;
72 // Finish up this request
73 }
74
75 }
默认情况下会走到第 22 行,调用 handler 对象的 process 方法,这里 handler 对象实际上是 Http11ConnectionHandler 类的实例,该对象的初始化过程是在 org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol对象的构造方法中:
public Http11Protocol() {
endpoint = new JIoEndpoint();
cHandler = new Http11ConnectionHandler(this);
((JIoEndpoint) endpoint).setHandler(cHandler);
setSoLinger(Constants.DEFAULT_CONNECTION_LINGER);
setSoTimeout(Constants.DEFAULT_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
setTcpNoDelay(Constants.DEFAULT_TCP_NO_DELAY);
}
所以需要到org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol类的静态内部类 Http11ConnectionHandler 中找到 process 方法的定义,但当前定义里面没有,这个方法是在其父类org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol.AbstractConnectionHandler中定义的:
1 public SocketState process(SocketWrapper<S> socket,
2 SocketStatus status) {
3 Processor<S> processor = connections.remove(socket.getSocket());
4
5 if (status == SocketStatus.DISCONNECT && processor == null) {
6 //nothing more to be done endpoint requested a close
7 //and there are no object associated with this connection
8 return SocketState.CLOSED;
9 }
10
11 socket.setAsync(false);
12
13 try {
14 if (processor == null) {
15 processor = recycledProcessors.poll();
16 }
17 if (processor == null) {
18 processor = createProcessor();
19 }
20
21 initSsl(socket, processor);
22
23 SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;
24 do {
25 if (status == SocketStatus.DISCONNECT &&
26 !processor.isComet()) {
27 // Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled
28 // Don't do this for Comet we need to generate an end
29 // event (see BZ 54022)
30 } else if (processor.isAsync() ||
31 state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) {
32 state = processor.asyncDispatch(status);
33 } else if (processor.isComet()) {
34 state = processor.event(status);
35 } else if (processor.isUpgrade()) {
36 state = processor.upgradeDispatch();
37 } else {
38 state = processor.process(socket);
39 }
40
41 if (state != SocketState.CLOSED && processor.isAsync()) {
42 state = processor.asyncPostProcess();
43 }
44
45 if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {
46 // Get the UpgradeInbound handler
47 UpgradeInbound inbound = processor.getUpgradeInbound();
48 // Release the Http11 processor to be re-used
49 release(socket, processor, false, false);
50 // Create the light-weight upgrade processor
51 processor = createUpgradeProcessor(socket, inbound);
52 inbound.onUpgradeComplete();
53 }
54 } while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END ||
55 state == SocketState.UPGRADING);
56
57 if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
58 // In the middle of processing a request/response. Keep the
59 // socket associated with the processor. Exact requirements
60 // depend on type of long poll
61 longPoll(socket, processor);
62 } else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {
63 // In keep-alive but between requests. OK to recycle
64 // processor. Continue to poll for the next request.
65 release(socket, processor, false, true);
66 } else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {
67 // Sendfile in progress. If it fails, the socket will be
68 // closed. If it works, the socket will be re-added to the
69 // poller
70 release(socket, processor, false, false);
71 } else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {
72 // Need to keep the connection associated with the processor
73 longPoll(socket, processor);
74 } else {
75 // Connection closed. OK to recycle the processor.
76 if (!(processor instanceof UpgradeProcessor)) {
77 release(socket, processor, true, false);
78 }
79 }
80 return state;
81 } catch(java.net.SocketException e) {
82 // SocketExceptions are normal
83 getLog().debug(sm.getString(
84 "abstractConnectionHandler.socketexception.debug"), e);
85 } catch (java.io.IOException e) {
86 // IOExceptions are normal
87 getLog().debug(sm.getString(
88 "abstractConnectionHandler.ioexception.debug"), e);
89 }
90 // Future developers: if you discover any other
91 // rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as
92 // above.
93 catch (Throwable e) {
94 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
95 // any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it
96 // with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on
97 // less-than-verbose logs.
98 getLog().error(
99 sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);
100 }
101 // Don't try to add upgrade processors back into the pool
102 if (!(processor instanceof UpgradeProcessor)) {
103 release(socket, processor, true, false);
104 }
105 return SocketState.CLOSED;
106 }
重点在第 38 行,调用 processor 的 process 方法处理 socket 。而 processor 对象在第 18 行通过 createProcessor 方法创建出来的,createProcessor 方法在当前类里面是抽象方法,默认情况下调用的具体实现类在上面提到的 Http11ConnectionHandler 类中:
1 @Override
2 protected Http11Processor createProcessor() {
3 Http11Processor processor = new Http11Processor(
4 proto.getMaxHttpHeaderSize(), (JIoEndpoint)proto.endpoint,
5 proto.getMaxTrailerSize());
6 processor.setAdapter(proto.adapter);
7 processor.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(proto.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
8 processor.setKeepAliveTimeout(proto.getKeepAliveTimeout());
9 processor.setConnectionUploadTimeout(
10 proto.getConnectionUploadTimeout());
11 processor.setDisableUploadTimeout(proto.getDisableUploadTimeout());
12 processor.setCompressionMinSize(proto.getCompressionMinSize());
13 processor.setCompression(proto.getCompression());
14 processor.setNoCompressionUserAgents(proto.getNoCompressionUserAgents());
15 processor.setCompressableMimeTypes(proto.getCompressableMimeTypes());
16 processor.setRestrictedUserAgents(proto.getRestrictedUserAgents());
17 processor.setSocketBuffer(proto.getSocketBuffer());
18 processor.setMaxSavePostSize(proto.getMaxSavePostSize());
19 processor.setServer(proto.getServer());
20 processor.setDisableKeepAlivePercentage(
21 proto.getDisableKeepAlivePercentage());
22 register(processor);
23 return processor;
24 }
此时的 processor 对象是 Http11Processor 类的实例,再看上一段提到的 processor.process 方法,最终会执行到 Http11Processor 类(因为该类中没有定义 process 方法)的父类org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor中的 process 方法。
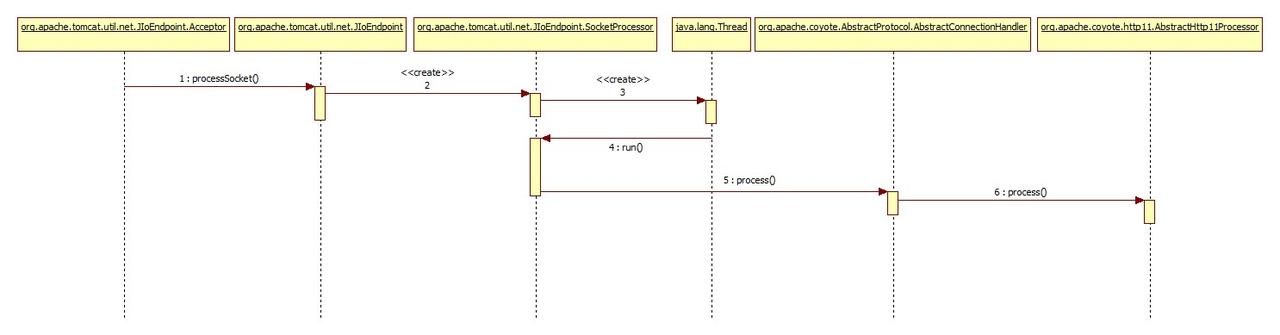
为了方便理解,下面的时序图列出从 Acceptor 线程的 run 方法到 AbstractHttp11Processor 类的 process 方法的关键方法调用过程:
1 @Override
2 public SocketState process(SocketWrapper<S> socketWrapper)
3 throws IOException {
4 RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();
5 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);
6
7 // Setting up the I/O
8 setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);
9 getInputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
10 getOutputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
11
12 // Flags
13 error = false;
14 keepAlive = true;
15 comet = false;
16 openSocket = false;
17 sendfileInProgress = false;
18 readComplete = true;
19 if (endpoint.getUsePolling()) {
20 keptAlive = false;
21 } else {
22 keptAlive = socketWrapper.isKeptAlive();
23 }
24
25 if (disableKeepAlive()) {
26 socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(0);
27 }
28
29 while (!error && keepAlive && !comet && !isAsync() &&
30 upgradeInbound == null && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
31
32 // Parsing the request header
33 try {
34 setRequestLineReadTimeout();
35
36 if (!getInputBuffer().parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {
37 if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
38 break;
39 }
40 }
41
42 if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
43 // 503 - Service unavailable
44 response.setStatus(503);
45 error = true;
46 } else {
47 // Make sure that connectors that are non-blocking during
48 // header processing (NIO) only set the start time the first
49 // time a request is processed.
50 if (request.getStartTime() < 0) {
51 request.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
52 }
53 keptAlive = true;
54 // Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
55 request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
56 // Currently only NIO will ever return false here
57 if (!getInputBuffer().parseHeaders()) {
58 // We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
59 // instead associate it with the socket
60 openSocket = true;
61 readComplete = false;
62 break;
63 }
64 if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
65 setSocketTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);
66 }
67 }
68 } catch (IOException e) {
69 if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
70 getLog().debug(
71 sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);
72 }
73 error = true;
74 break;
75 } catch (Throwable t) {
76 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
77 UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();
78 if (logMode != null) {
79 String message = sm.getString(
80 "http11processor.header.parse");
81 switch (logMode) {
82 case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:
83 message += sm.getString(
84 "http11processor.fallToDebug");
85 //$FALL-THROUGH$
86 case INFO:
87 getLog().info(message);
88 break;
89 case DEBUG:
90 getLog().debug(message);
91 }
92 }
93 // 400 - Bad Request
94 response.setStatus(400);
95 adapter.log(request, response, 0);
96 error = true;
97 }
98
99 if (!error) {
100 // Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
101 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
102 try {
103 prepareRequest();
104 } catch (Throwable t) {
105 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
106 if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
107 getLog().debug(sm.getString(
108 "http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
109 }
110 // 400 - Internal Server Error
111 response.setStatus(400);
112 adapter.log(request, response, 0);
113 error = true;
114 }
115 }
116
117 if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {
118 keepAlive = false;
119 } else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&
120 socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {
121 keepAlive = false;
122 }
123
124 // Process the request in the adapter
125 if (!error) {
126 try {
127 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
128 adapter.service(request, response);
129 // Handle when the response was committed before a serious
130 // error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both
131 // set the status to 500 and set the errorException.
132 // If we fail here, then the response is likely already
133 // committed, so we can't try and set headers.
134 if(keepAlive && !error) { // Avoid checking twice.
135 error = response.getErrorException() != null ||
136 (!isAsync() &&
137 statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus()));
138 }
139 setCometTimeouts(socketWrapper);
140 } catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
141 error = true;
142 } catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {
143 error = true;
144 // The response should not have been committed but check it
145 // anyway to be safe
146 if (!response.isCommitted()) {
147 response.reset();
148 response.setStatus(500);
149 response.setHeader("Connection", "close");
150 }
151 } catch (Throwable t) {
152 ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
153 getLog().error(sm.getString(
154 "http11processor.request.process"), t);
155 // 500 - Internal Server Error
156 response.setStatus(500);
157 adapter.log(request, response, 0);
158 error = true;
159 }
160 }
161
162 // Finish the handling of the request
163 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
164
165 if (!isAsync() && !comet) {
166 if (error) {
167 // If we know we are closing the connection, don't drain
168 // input. This way uploading a 100GB file doesn't tie up the
169 // thread if the servlet has rejected it.
170 getInputBuffer().setSwallowInput(false);
171 }
172 endRequest();
173 }
174
175 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
176
177 // If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
178 // and error, and update the statistics counter
179 if (error) {
180 response.setStatus(500);
181 }
182 request.updateCounters();
183
184 if (!isAsync() && !comet || error) {
185 getInputBuffer().nextRequest();
186 getOutputBuffer().nextRequest();
187 }
188
189 if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
190 if(endpoint.getSoTimeout() > 0) {
191 setSocketTimeout(endpoint.getSoTimeout());
192 } else {
193 setSocketTimeout(0);
194 }
195 }
196
197 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
198
199 if (breakKeepAliveLoop(socketWrapper)) {
200 break;
201 }
202 }
203
204 rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
205
206 if (error || endpoint.isPaused()) {
207 return SocketState.CLOSED;
208 } else if (isAsync() || comet) {
209 return SocketState.LONG;
210 } else if (isUpgrade()) {
211 return SocketState.UPGRADING;
212 } else {
213 if (sendfileInProgress) {
214 return SocketState.SENDFILE;
215 } else {
216 if (openSocket) {
217 if (readComplete) {
218 return SocketState.OPEN;
219 } else {
220 return SocketState.LONG;
221 }
222 } else {
223 return SocketState.CLOSED;
224 }
225 }
226 }
227 }
从这个方法中可以清晰的看出解析请求的过程:第 7 到 10 行从 Socket 中获取输入输出流,第 32 到 97 行解析请求行和请求头,第 99 到 115 行校验和解析请求头中的属性,第 125 到 160 行调用适配器的 service 方法,第 172 行请求处理结束。
上面就是根据 Http 协议解析请求的总体流程。要理解上面提到的请求行、请求头等术语,需要熟悉 Http 协议,这里简单介绍下 Http 协议中的标准请求信息数据的格式:
请求信息包括以下三条
- 请求行(request line)
例如GET /images/logo.gif HTTP/1.1,表示从/images目录下请求logo.gif这个文件。
- 请求头(request header),空行
例如Accept-Language: en
- 其他消息体
请求行和标题必须以<CR><LF>作为结尾。空行内必须只有<CR><LF>而无其他空格。在 HTTP/1.1 协议中,所有的请求头,除 Host 外,都是可选的。
请求行、请求头数据的格式具体看 Http 协议中的描述。所以在从输入流中读取到字节流数据之后必须按照请求行、请求头、消息体的顺序来解析。
这里以请求行数据的解析为例,在 Http 协议中该行内容格式为:
Request-Line = Method SP Request-URI SP HTTP-Version CRLF
即请求类型、要访问的资源( URI )以及使用的HTTP版本,中间以特殊字符空格来分隔,以\r\n字符结尾。
在上面列出的 AbstractHttp11Processor 类的 process 代码中的第 36 行,会调用抽象方法 getInputBuffer() ,当前该抽象方法的具体实现在子类org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor中,该方法返回的是该类的实例变量 inputBuffer :
protected AbstractInputBuffer<Socket> getInputBuffer() {
return inputBuffer;
}
该实例变量在 Http11Processor 的构造方法中会被初始化:
public Http11Processor(int headerBufferSize, JIoEndpoint endpoint,
int maxTrailerSize) {
super(endpoint);
inputBuffer = new InternalInputBuffer(request, headerBufferSize);
request.setInputBuffer(inputBuffer);
outputBuffer = new InternalOutputBuffer(response, headerBufferSize);
response.setOutputBuffer(outputBuffer);
initializeFilters(maxTrailerSize);
}
所以 AbstractHttp11Processor 类的 process 方法的 36 行 getInputBuffer().parseRequestLine() 将会调用org.apache.coyote.http11.InternalInputBuffer类中的 parseRequestLine 方法:
1 public boolean parseRequestLine(boolean useAvailableDataOnly)
2
3 throws IOException {
4
5 int start = 0;
6
7 //
8 // Skipping blank lines
9 //
10
11 byte chr = 0;
12 do {
13
14 // Read new bytes if needed
15 if (pos >= lastValid) {
16 if (!fill())
17 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
18 }
19
20 chr = buf[pos++];
21
22 } while ((chr == Constants.CR) || (chr == Constants.LF));
23
24 pos--;
25
26 // Mark the current buffer position
27 start = pos;
28
29 //
30 // Reading the method name
31 // Method name is always US-ASCII
32 //
33
34 boolean space = false;
35
36 while (!space) {
37
38 // Read new bytes if needed
39 if (pos >= lastValid) {
40 if (!fill())
41 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
42 }
43
44 // Spec says no CR or LF in method name
45 if (buf[pos] == Constants.CR || buf[pos] == Constants.LF) {
46 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
47 sm.getString("iib.invalidmethod"));
48 }
49 // Spec says single SP but it also says be tolerant of HT
50 if (buf[pos] == Constants.SP || buf[pos] == Constants.HT) {
51 space = true;
52 request.method().setBytes(buf, start, pos - start);
53 }
54
55 pos++;
56
57 }
58
59
60 // Spec says single SP but also says be tolerant of multiple and/or HT
61 while (space) {
62 // Read new bytes if needed
63 if (pos >= lastValid) {
64 if (!fill())
65 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
66 }
67 if (buf[pos] == Constants.SP || buf[pos] == Constants.HT) {
68 pos++;
69 } else {
70 space = false;
71 }
72 }
73
74 // Mark the current buffer position
75 start = pos;
76 int end = 0;
77 int questionPos = -1;
78
79 //
80 // Reading the URI
81 //
82
83 boolean eol = false;
84
85 while (!space) {
86
87 // Read new bytes if needed
88 if (pos >= lastValid) {
89 if (!fill())
90 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
91 }
92
93 // Spec says single SP but it also says be tolerant of HT
94 if (buf[pos] == Constants.SP || buf[pos] == Constants.HT) {
95 space = true;
96 end = pos;
97 } else if ((buf[pos] == Constants.CR)
98 || (buf[pos] == Constants.LF)) {
99 // HTTP/0.9 style request
100 eol = true;
101 space = true;
102 end = pos;
103 } else if ((buf[pos] == Constants.QUESTION)
104 && (questionPos == -1)) {
105 questionPos = pos;
106 }
107
108 pos++;
109
110 }
111
112 request.unparsedURI().setBytes(buf, start, end - start);
113 if (questionPos >= 0) {
114 request.queryString().setBytes(buf, questionPos + 1,
115 end - questionPos - 1);
116 request.requestURI().setBytes(buf, start, questionPos - start);
117 } else {
118 request.requestURI().setBytes(buf, start, end - start);
119 }
120
121 // Spec says single SP but also says be tolerant of multiple and/or HT
122 while (space) {
123 // Read new bytes if needed
124 if (pos >= lastValid) {
125 if (!fill())
126 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
127 }
128 if (buf[pos] == Constants.SP || buf[pos] == Constants.HT) {
129 pos++;
130 } else {
131 space = false;
132 }
133 }
134
135 // Mark the current buffer position
136 start = pos;
137 end = 0;
138
139 //
140 // Reading the protocol
141 // Protocol is always US-ASCII
142 //
143
144 while (!eol) {
145
146 // Read new bytes if needed
147 if (pos >= lastValid) {
148 if (!fill())
149 throw new EOFException(sm.getString("iib.eof.error"));
150 }
151
152 if (buf[pos] == Constants.CR) {
153 end = pos;
154 } else if (buf[pos] == Constants.LF) {
155 if (end == 0)
156 end = pos;
157 eol = true;
158 }
159
160 pos++;
161
162 }
163
164 if ((end - start) > 0) {
165 request.protocol().setBytes(buf, start, end - start);
166 } else {
167 request.protocol().setString("");
168 }
169
170 return true;
171
172 }
先看这个方法中第 16 行,调用了当前类的 fill 方法:
protected boolean fill() throws IOException {
return fill(true);
}
里面调用了重载方法 fill :
1 protected boolean fill(boolean block) throws IOException {
2
3 int nRead = 0;
4
5 if (parsingHeader) {
6
7 if (lastValid == buf.length) {
8 throw new IllegalArgumentException
9 (sm.getString("iib.requestheadertoolarge.error"));
10 }
11
12 nRead = inputStream.read(buf, pos, buf.length - lastValid);
13 if (nRead > 0) {
14 lastValid = pos + nRead;
15 }
16
17 } else {
18
19 if (buf.length - end < 4500) {
20 // In this case, the request header was really large, so we allocate a
21 // brand new one; the old one will get GCed when subsequent requests
22 // clear all references
23 buf = new byte[buf.length];
24 end = 0;
25 }
26 pos = end;
27 lastValid = pos;
28 nRead = inputStream.read(buf, pos, buf.length - lastValid);
29 if (nRead > 0) {
30 lastValid = pos + nRead;
31 }
32
33 }
34
35 return (nRead > 0);
36
37 } }
在这里可以看到从输入流中读取数据到缓冲区 buf 。按照上面列出的请求行数据格式,从字符流中将会按顺序得到请求的类型( method )、请求的 URI 和 Http 版本。具体实现流程如下:
在org.apache.coyote.http11.InternalInputBuffer类中的 parseRequestLine 方法,第 34 到 57 行根据请求头协议的格式,从中取出表示请求方法的字节数据并设置到内置实例变量 request 。第 60 到 72 行解析 method 和 uri 之间的空格字节 SP ,第 83 到 119 行读取表示请求的 URI 的字节数据并放到 request 变量中。第 122 到 133 行解析 uri 和 http 协议版本之间的空格字节 SP ,第 144 到第 168 行读取表示请求的 Http 协议版本的字节数据并放到 request 变量中。
以上是根据 Http 协议解析请求行( request line )的代码实现部分,解析请求头的部分见 InternalInputBuffer 类的 parseHeader 方法,不再赘述。
至此可以看到在 Tomcat 中如何从一次 Socket 连接中取出请求的数据,将这些原始的字符流数据转换成初步可以理解的 Tomcat 内置对象org.apache.coyote.Request的。