前言
简介
在dubbo中,我们可以使用两种方式引用远程服务,一种是使用服务直连的方式引用服务[仅适合测试或调试环境],还有一种是基于注册中心进行服务引用,一般使用zookeeper做为注册中心,像我们公司就是使用的zk做为注册中心来进行服务的注册。
引入时机
万事俱备,只欠东风,这里时间很重要,正所谓,谋事在人,成事在天,程序和生活比起来更加有人情味的一点就在于他的可预见性,对于服务的引入有两个固定的时机,一个是Spring容器中调用ReferenceBean 时,另外一个是ReferenceBean 被注入到其他类中引用时,他们两个的区别在于,第一个是饿汉式,另外一个是懒汉式,具体可以参考一下单例模式,下面,我们看一下对于服务引入这一块的源码
源码分析
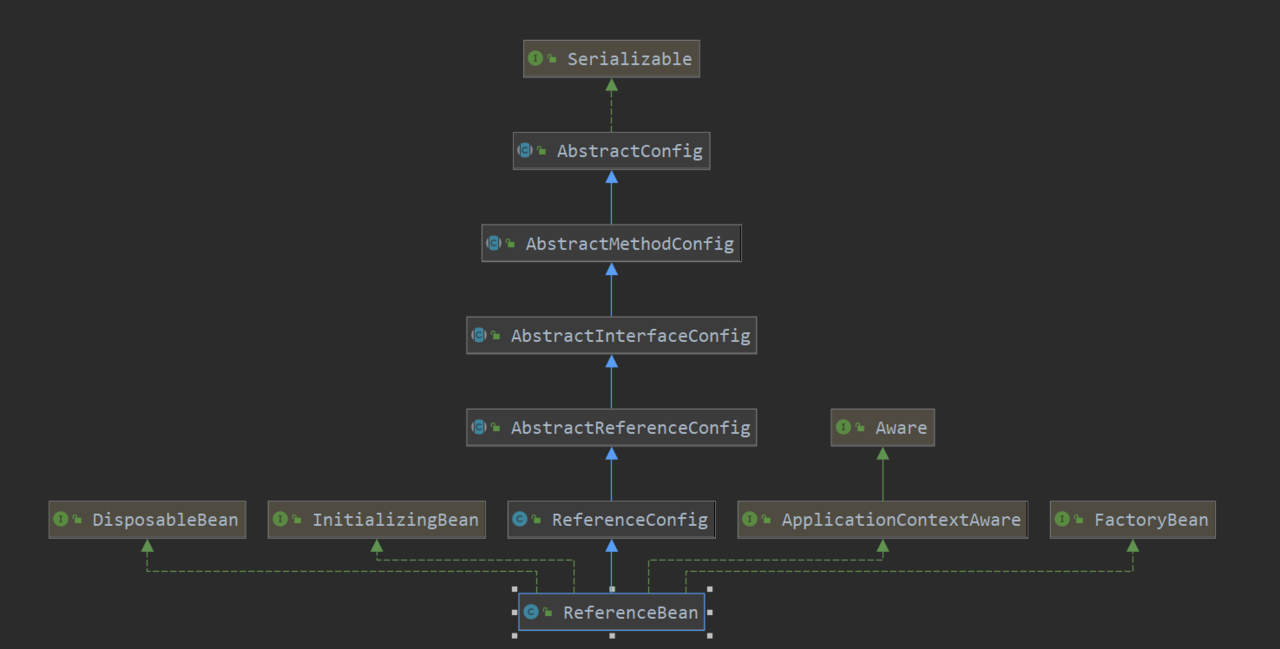
服务引入的入口方法是ReferenceBean,dubbo使用了spring的自定义标签解析,实体类ReferenceBean对应标签 dubbo:reference,话不多说,我们先看一下ReferenceBean的类结构图,然后在正式进入分析环节
这里我是直接用dubbo源码自带的demo进行调试,服务引用的入口方法为 ReferenceBean 的 getObject 方法,这个方法定义在 Spring 的 FactoryBean 接口中,ReferenceBean 实现了这个方法
#ReferenceBean.java
@Override
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return get();
}
//ReferenceConfig.java
public synchronized T get() {
if (destroyed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Already destroyed!");
}
if (ref == null) {
init();
}
return ref;
}
这里官网有一段说明, 2.6.4 及以下版本的 getObject 方法进行调试到if (ref == null)时,ref!=null,可以修改 IDEA Enable ‘toString’ object view,具体请查看官方文档
由上面的代码可以看出,主要执行逻辑在init()
# ReferenceConfig.java
private void init() {
#避免重复初始化
if (initialized) {
return;
}
initialized = true;
#interfaceName 你所暴露的接口 验证接口是否合理
if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:reference interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!");
}
# 检测 consumer #变量是否为空,为空则创建,appendPropertie会填充我们配置的标签的bean属性
checkDefault();
appendProperties(this);
# 是否使用泛化接口,默认使用<dubbo:consumer>的Generic
if (getGeneric() == null && getConsumer() != null) {
setGeneric(getConsumer().getGeneric());
}
# 检查是否为泛化类
if (ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(getGeneric())) {
interfaceClass = GenericService.class;
} else {
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods);
}
# 从系统变量中获取与接口名对应的属性值
String resolve = System.getProperty(interfaceName);
String resolveFile = null;
if (resolve == null || resolve.length() == 0) {
# 直连提供者->服务多时可以使用属性dubbo.resolve.file指定映射文件
resolveFile = System.getProperty("dubbo.resolve.file");
if (resolveFile == null || resolveFile.length() == 0) {
File userResolveFile = new File(new File(System.getProperty("user.home")), "dubbo-resolve.properties");
if (userResolveFile.exists()) {
resolveFile = userResolveFile.getAbsolutePath();
}
}
if (resolveFile != null && resolveFile.length() > 0) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(new File(resolveFile));
properties.load(fis);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unload " + resolveFile + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
try {
if (null != fis) fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
resolve = properties.getProperty(interfaceName);
}
}
if (resolve != null && resolve.length() > 0) {
url = resolve;
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
if (resolveFile != null) {
logger.warn("Using default dubbo resolve file " + resolveFile + " replace " + interfaceName + "" + resolve + " to p2p invoke remote service.");
} else {
logger.warn("Using -D" + interfaceName + "=" + resolve + " to p2p invoke remote service.");
}
}
}
if (consumer != null) {
if (application == null) {
application = consumer.getApplication();
}
if (module == null) {
module = consumer.getModule();
}
if (registries == null) {
registries = consumer.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = consumer.getMonitor();
}
}
if (module != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = module.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = module.getMonitor();
}
}
if (application != null) {
if (registries == null) {
registries = application.getRegistries();
}
if (monitor == null) {
monitor = application.getMonitor();
}
}
checkApplication(); # 检测 Application 合法性
checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass); #检测 本地存根 合法性
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
resolveAsyncInterface(interfaceClass, map);
Map<Object, Object> attributes = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
map.put(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE);
map.put(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, Version.getProtocolVersion());
map.put(Constants.TIMESTAMP_KEY, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
if (ConfigUtils.getPid() > 0) {
map.put(Constants.PID_KEY, String.valueOf(ConfigUtils.getPid()));
}# 非泛化服务
if (!isGeneric()) {
String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version);
if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) {
map.put("revision", revision);
}
#获取接口方法列表,并添加到 map 中 Wrapper.getWrapper是一个包装类
String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames();
if (methods.length == 0) {
logger.warn("NO method found in service interface " + interfaceClass.getName());
map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE);
} else {
map.put("methods", StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), ","));
}
}
map.put(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName);
# 将 ApplicationConfig、ConsumerConfig、ReferenceConfig 等对象的字段信息添加到 map 中
appendParameters(map, application);
appendParameters(map, module);
appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY);
appendParameters(map, this);
String prefix = StringUtils.getServiceKey(map);
if (methods != null && !methods.isEmpty()) {
for (MethodConfig method : methods) {
appendParameters(map, method, method.getName());
String retryKey = method.getName() + ".retry";
if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) {
String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey);
if ("false".equals(retryValue)) {
# 添加重试次数配置 methodName.retries
map.put(method.getName() + ".retries", "0");
}
}
#添加 MethodConfig 中的“属性”字段到 attributes
# 比如 onreturn、onthrow、oninvoke 等
appendAttributes(attributes, method, prefix + "." + method.getName());
checkAndConvertImplicitConfig(method, map, attributes);
}
}
# 获取服务消费者 ip 地址
String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY);
if (hostToRegistry == null || hostToRegistry.length() == 0) {
hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost(); // 默认ip 地址=本机
} else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property:" + Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY + ", value:" + hostToRegistry);
}
map.put(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry);
#attributes are stored by system context.
StaticContext.getSystemContext().putAll(attributes);
# 存储 attributes 到系统上下文中
ref = createProxy(map);
# 根据服务名,ReferenceConfig,代理类构建 ConsumerModel,
# 并将 ConsumerModel 存入到 ApplicationModel 中
ConsumerModel consumerModel = new ConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref, interfaceClass.getMethods());
ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), consumerModel);
}
上文中ref主要是由createProxy创建的一个代理类,在init()方法中,createProxy接受了一个封装了我们各种配置信息的map键值对,我们主要看一下createProxy()方法解析服务消费者ip,以及怎么样调用 createProxy 创建代理对象
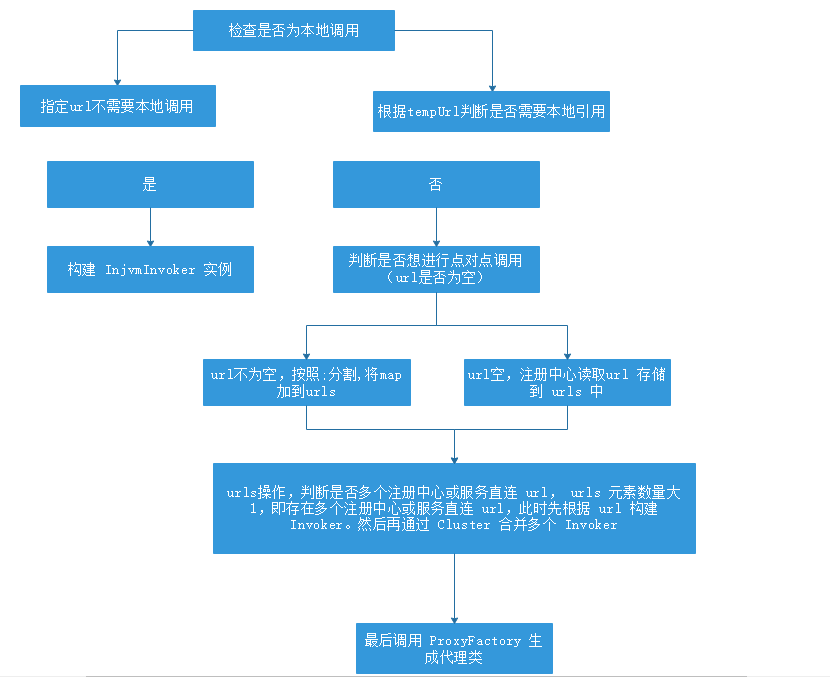
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
# 注意!!! 这里的URL是org.apache.dubbo.common包下的
URL tmpUrl = new URL("temp", "localhost", 0, map);
final boolean isJvmRefer;
if (isInjvm() == null) {
#如果指定了url,不要做本地引用
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { # if a url is specified, don't do local reference
isJvmRefer = false;
# 根据tepUrl判断是否需要本地引用
} else if (InjvmProtocol.getInjvmProtocol().isInjvmRefer(tmpUrl)) {
# by default, reference local service if there is
isJvmRefer = true;
} else {
isJvmRefer = false;
}
} else {
isJvmRefer = isInjvm().booleanValue();
}
# 本地引用
if (isJvmRefer) {
# 创建服务引用 URL 对象
URL url = new URL(Constants.LOCAL_PROTOCOL, NetUtils.LOCALHOST, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map);
# 调用 refer 方法构建 InjvmInvoker 实例
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
} else {
# url 不为空,表明用户可能想进行点对点调用
if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { # user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address.
String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url);
# 当需要配置多个 url 时,用;进行分割
if (us != null && us.length > 0) {
for (String u : us) {
URL url = URL.valueOf(u);
if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) {
url = url.setPath(interfaceName);
}
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
} else {
urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map));
}
}
}
} else { #从注册中心中加载Url
List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false);
if (us != null && !us.isEmpty()) {
for (URL u : us) {
URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u);
if (monitorUrl != null) {
map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString()));
}
urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map)));
}
}
if (urls.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config.");
}
}
# 单个注册中心或服务提供者(服务直连,下同)
if (urls.size() == 1) {
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
} else { # 多个注册中心或多个服务提供者,或者两者混合
List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>();
URL registryURL = null;
for (URL url : urls) {
invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url));
if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) {
registryURL = url; # use last registry url
}
}
if (registryURL != null) { # registry url is available
# use AvailableCluster only when register's cluster is available
URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME);
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers));
} else { # not a registry url
invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers));
}
}
}
Boolean c = check;
if (c == null && consumer != null) {
c = consumer.isCheck();
}
if (c == null) {
c = true; # default true
}
if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
# make it possible for consumer to retry later if provider is temporarily unavailable
initialized = false;
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion());
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl());
}
# create service proxy 生成代理类 调用的是AbstractProxyFactory.getProxy
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}
Invoker 的构建过程以及代理类的过程
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
# 序列化
optimizeSerialization(url);
# 创建 DubboInvoker
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
上述代码中的getClients()方法用于获取客户端的实例,实例类型为 ExchangeClient,ExchangeClient默认会调用NettyClient
# DubboProtocol.java
private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url) {
# 是否共享连接
boolean service_share_connect = false;
# 获取连接数,默认为0,表示未配置
int connections = url.getParameter(Constants.CONNECTIONS_KEY, 0);
# 如果未配置 connections,则共享连接
if (connections == 0) {
service_share_connect = true;
connections = 1;
}
ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections];
for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) {
if (service_share_connect) {
# 获取共享客户端
clients[i] = getSharedClient(url);
} else {
# 初始化新的客户端
clients[i] = initClient(url);
}
}
return clients;
}
默认情况下,使用共享客户端实例。getSharedClient()也会调用 initClient 方法
# DubboProtocol.java
private ExchangeClient getSharedClient(URL url) {
# key = 调用地址
String key = url.getAddress();
ReferenceCountExchangeClient client = referenceClientMap.get(key);
if (client != null) {
if (!client.isClosed()) {
# 增加引用计数
client.incrementAndGetCount();
return client;
} else {
referenceClientMap.remove(key);
}
}
# putIfAbsent 如果传入key对应的value已经存在,就返回存在的value,不进行替换。如果不存在,就添加key和value,返回null
locks.putIfAbsent(key, new Object());
synchronized (locks.get(key)) {
if (referenceClientMap.containsKey(key)) {
return referenceClientMap.get(key);
}
# 创建 ExchangeClient 客户端
ExchangeClient exchangeClient = initClient(url);
# 装饰模式
client = new ReferenceCountExchangeClient(exchangeClient, ghostClientMap);
referenceClientMap.put(key, client);
ghostClientMap.remove(key);
locks.remove(key);
return client;
}
}
先访问缓存,若缓存未命中,则通过 initClient 方法创建新的 ExchangeClient 实例,并将该实例传给 ReferenceCountExchangeClient 构造方法创建一个带有引用计数功能的 ExchangeClient 实例,我们看一下initClient(url)
# DubboProtocol.java
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) {
// 获取客户端类型,默认为 netty
String str = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT));
// 添加编解码和心跳包参数到 url 中
url = url.addParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME);
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT));
// 检测客户端类型是否存在,不存在则抛出异常
if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) {
throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: ...");
}
ExchangeClient client;
try {
// 获取 lazy 配置,并根据配置值决定创建的客户端类型
if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) {
// 创建懒加载 ExchangeClient 实例
client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler);
} else {
// 创建普通 ExchangeClient 实例
client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler);
}
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service...");
}
return client;
}
# Exchangers
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
}
url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange");
# 获取 Exchanger 实例,默认为 HeaderExchangeClient
return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
}
主要方法getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler);
# HeaderExchanger.java
@Override
# 1. 创建 HeaderExchangeHandler 对象 -> new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler)
# 2. 创建 DecodeHandler 对象 -> new DecodeHandler()
# 3. 通过 Transporters 构建 Client 实例 -> Transporters.connect()
# 4. 创建 HeaderExchangeClient 对象 -> new HeaderExchangeClient()
public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true);
}
PS:这里实现了Exchanger
# Exchanger.java
/**
* connect.
*
* @param url
* @param handler
* @return message channel
*/
@Adaptive({Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY})
ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
Dubbo提供了一种SPI的机制用于动态的加载扩展类,Adaptive机制在运行时动态的选用扩展类来提供服务,Adaptive注解可以用于接口的某个子类上,也可以用于接口方法上。如果用在接口的子类上,则表示Adaptive机制的实现会按照该子类的方式进行自定义实现;如果用在方法上,则表示Dubbo会为该接口自动生成一个子类,并且按照一定的格式重写该方法,而其余没有标注@Adaptive注解的方法将会默认抛出异常
# Transporters 的 connect 方法
public static Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
ChannelHandler handler;
if (handlers == null || handlers.length == 0) {
handler = new ChannelHandlerAdapter();
} else if (handlers.length == 1) {
handler = handlers[0];
} else {
// 如果 handler 数量大于1,则创建一个 ChannelHandler 分发器
handler = new ChannelHandlerDispatcher(handlers);
}
// 获取 Transporter 自适应拓展类 默认加载 NettyTransporter,并调用 connect 方法生成 Client 实例
return getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
}
# getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
public Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler listener) throws RemotingException {
// 创建 NettyClient 对象
return new NettyClient(url, listener);
}