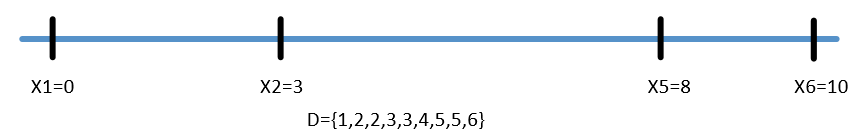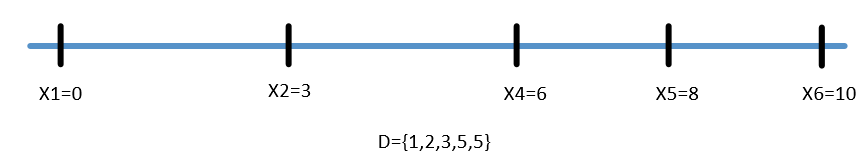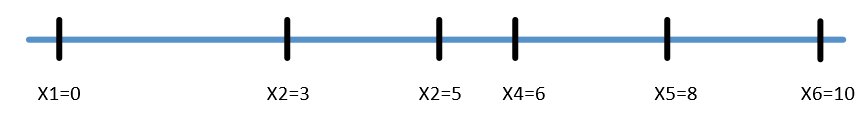前言
大家好,这是本人算法系列最后一篇,介绍回溯算法。感谢大家支持,希望指正。
算法介绍
回溯算法相当于穷举搜索的巧妙实现,但是性能一般不理想。回溯算法中经常使用裁剪,
裁剪,即在一步删除一大组可能性的做法。
下面以两个例子进行说明。
高速公路重建问题
问题描述
设给定N个点P1,P2,…….,PN,它们位于X轴上。Xi是Pi点的X坐标。进一步假设X1=0以及这些点从左到右给出。着N个点确定,在每一对,点间的N(N-1)/2个,形如|Xi – Xj|(i !=j)的距离。收费公路重建问题就是由这些距离重构一个点集。
举例分析
以书上例子说明: 令D是距离集合,且D={1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,5,5,5,6,7,8,10},由D=15可以知道N=6,若设X1=0,则有x6=10,x5=8。
下面以X1=0,x6=10,x5=8为初始状态进行尝试。
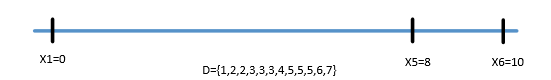 在这里输入图片标题
在这里输入图片标题
目前边集中最大值为7,要么x4=7,要么x2=3,我们分别进行尝试
尝试x4=7,裁剪相应边集D

简单推测:
目前边集中最大值为6,要么x3=6,要么x2=4. 若x3=6,x4-x3=1,而剩余边集D中没有1,即x3=6不成立
如果x2=4,x2-xo=4和x5-x2=4,而剩余边集D中仅有1个4,即x2=4也不成立。 由此可知,x4=7不成立我们需要进行回溯
尝试x4=7不成立,回溯到初始状态
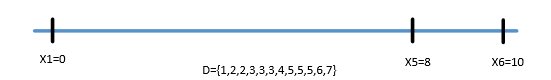
尝试x2=3 裁剪相应边集D
简单推测: 目前边集中最大值为6,要么x4=6,要么x2=4.
如果x2=4,x2-xo=4和x5-x2=4,而剩余边集D中仅有1个4,即x2=4不成立。
若x4=6,x10-x4=4,x5-x4=8-6=2,x4-x2=6-3=3,x4-x0=6-0=6,均在剩余边集合D中,x4=6 可选。
尝试x2=3 基础上尝试x4=6,裁剪相应边集合D
简单推测:
目前边集中最大值为5,要么x3=5.
X3-x1=5-0=5,x3-x2=5-3=2,x4-x5=6-5=1,x5-x3=8-5=3,x6-x3=10-5=5,整好所有边集均清空,我们找到最终答案如下:
核心代码实现
/**
* @param x
* 结果点集合
* @param distSet
* 边的优先队列,注意队列从大到小
* @param n
* 根据边集大小计算出来的 预计点个数, n(n-1)/2=distSet.size();
* @return
*/
public static boolean turnpike(int[] x, PriorityQueue<Integer> distSet, int n) {
// 倒序排列边集合
x[1] = 0;
x[n] = distSet.poll();
x[n - 1] = distSet.poll();
if (distSet.contains(x[n] - x[n - 1])) {
distSet.remove(new Integer(x[n] - x[n - 1]));
return place(x, distSet, n, 2, n - 2);
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 重建高速公路-回溯算法核心
* @param x 结果集合
* @param distSet 剩余边集合 从大到小构建的堆
* @param n 预计包含的点集合
* @param left 本次尝试的左边界
* @param right 本次尝试的右边开始点
*/
private static boolean place(int[] x, PriorityQueue<Integer> distSet, int n, int left, int right) {
int dmax = 0;
boolean found = false;
if (distSet.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
dmax = distSet.peek();
// 尝试x[right]为 dmax
if (CheckIfRight(x, distSet, n, left, right, dmax)) {
x[right] = dmax;
for (int j = 1; j < left; j++) {
distSet.remove(new Integer(Math.abs(x[j] - x[right])));
}
for (int j = right + 1; j <= n; j++) {
distSet.remove(new Integer(Math.abs(x[j] - x[right])));
}
found = place(x, distSet, n, left, right - 1);
if (!found) {
for (int j = 1; j < left; j++) {
distSet.add(new Integer(Math.abs(x[j] - x[right])));
}
for (int j = right + 1; j <= n; j++) {
distSet.add(new Integer(Math.abs(x[j] - x[right])));
}
}
}
// x[left]=x[n]-dmax
if (!found && CheckIfleft(x, distSet, n, left, right, dmax)) {
x[left] = x[n] - dmax;
for (int j = 1; j < left; j++) {
distSet.remove(new Integer(Math.abs(x[n] - dmax - x[j])));
}
for (int j = right + 1; j <= n; j++) {
distSet.remove(new Integer(Math.abs(x[n] - dmax - x[j])));
}
found = place(x, distSet, n, left + 1, right);
if (!found) {
for (int j = 1; j < left; j++) {
distSet.add(new Integer(Math.abs(x[n] - dmax - x[j])));
}
for (int j = right + 1; j <= n; j++) {
distSet.add(new Integer(Math.abs(x[n] - dmax - x[j])));
}
}
}
return found;
}
正序全排列问题
举例说明
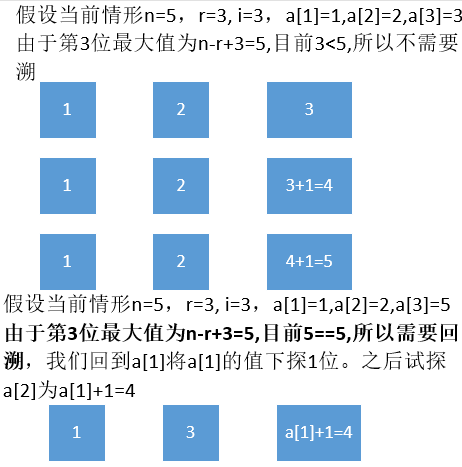
例如 n为5,r为3,输出 输出:
[1, 2, 3] [1, 2, 4] [1, 2, 5]
[1, 3, 4] [1, 3, 5]
[1, 4, 5]
[2, 3, 4] [2, 3, 5]
[2, 4, 5]
[3, 4, 5]
分析
第1位最大值为n-r+1=3,
第2位的最大值为n-r+2=4
第3位的最大值为n-r+3=5
可以推测出第i位最大值为n-r+i,也就是每一位超过相应值需要回溯。
实现原理
1、 前提 数组a作为中间变量,存储可能的临时结果。 a[1]标示第一位,a[2]标示第2位,…,a[r]表示第r位 resultIndex 表示当前尝试位数,它从1开始,到r。
2、 步骤
2.1 我们从a[1]=1开始到a[1]>n-r+1结束。当resultIndex=r时存储到最终结果队列。
2.2 分支操作说明
- 当resultIndex<r 我们进行下探,即a[resultIndex+1]=a[resultIndex]+1
- 当resultIndexr==r时进行末位试探,即a[resultIndex]=a[resultIndex]+1
- 当 a[resultIndex+1]>n-r+resultIndex,进行回溯,即resultIndex–;a[resultIndex]=a[resultIndex]+1;
- 当resultIndex==r 并且 a[resultIndex+1]==n-r+resultIndex,进行末位回溯 即resultIndex–;a[resultIndex]=a[resultIndex]+1;
图例说明
代码实现
/**
* 核心处理方法
* @param selectIndexList 存储结果
*/
private void combOrder(List<int[]> selectIndexList) {
if(r==0){
return ;
}
if(r==1){
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
selectIndexList.add(new int[] { i });
}
return;
}
int resultIndex=1;
a[1]=1;
while(a[1]<=(n-r+1)){//根据第一位进行裁剪,第一位取值为1<a[1]<n-r+1 列入5个数选3个 第一位最大为5-3+1=3
if(resultIndex<r){
if(a[resultIndex]<=n-r+resultIndex){
a[resultIndex+1] = a[resultIndex]+1;
resultIndex++;
}else{// 已经超过每一位的最大值 n-r+resultIndex,进行回溯
resultIndex--;
a[resultIndex]=a[resultIndex]+1;
}
}else if(resultIndex==r){
int[] selectIndex = new int[r];
selectIndexList.add(selectIndex);
for (int j = 1; j <= r; j++) {//存储结果
selectIndex[j - 1] = a[j]-1;
}
if (a[resultIndex]==n) { // 若当前搜索结果为1,表示本次搜素完成,进行回溯 此时条件相当为 ri+a[ri]==r+1 因为ri=r所以简化啦
resultIndex--;
a[resultIndex] = a[resultIndex]+1; // 回溯
} else {
a[resultIndex] = a[resultIndex]+1; // 搜索到下一个数
}
}
}
}
总结
- 回溯算法,一般需要分析 ,推导出回溯的条件。
- 回溯算法,效率一般比较低下。