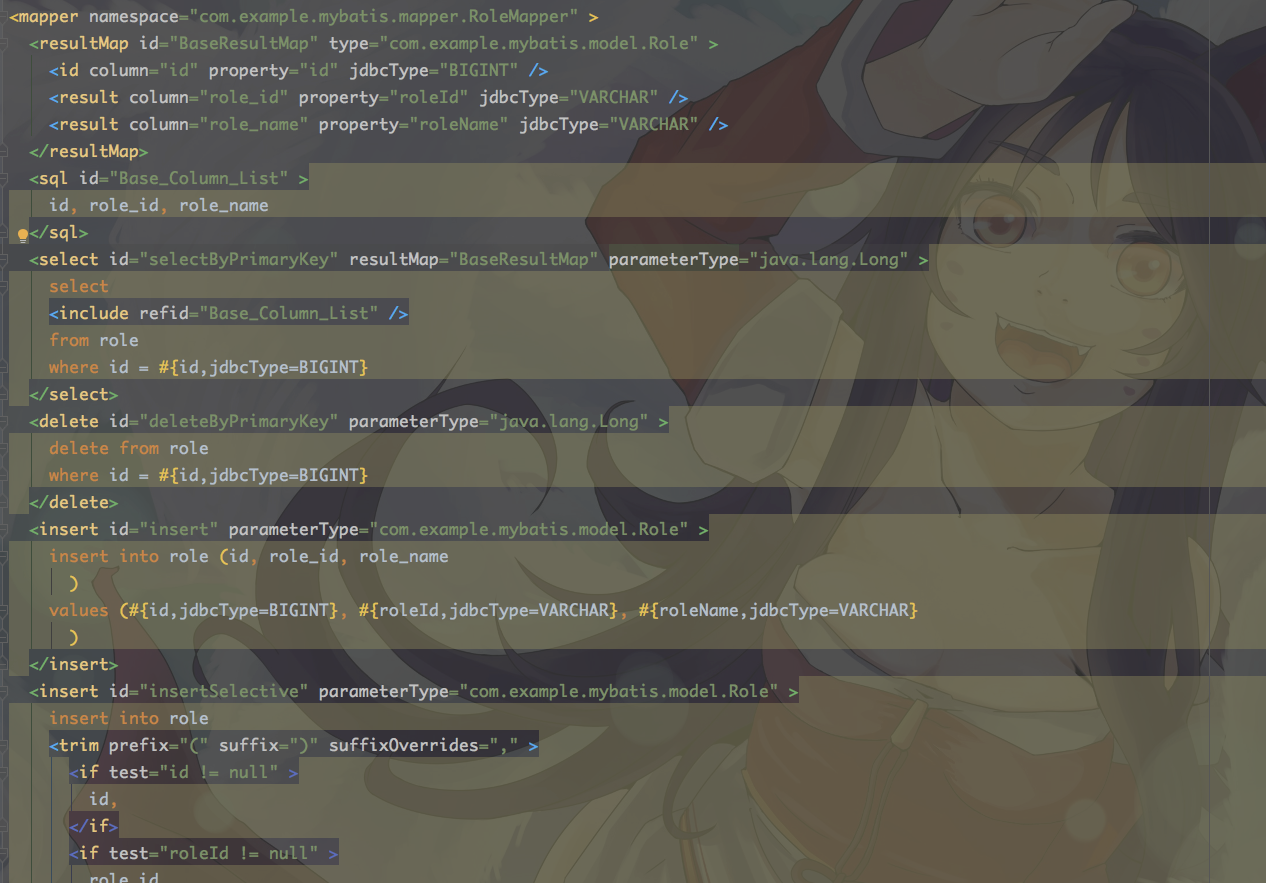
本文源代码来源于mybatis-spring-boot-starter的2.1.2版本
一、前言
前面我们说了MapperPoxy的扫描和构建,它会被SqlSession的getMapper()方法调用生成。而SqlSession被创建时候需要一个非常重要的参数Configuration(Mybatis-config.xml和所有的Mapper.xml文件的配置项),它是构建Mybatis运行的核心对象。那么MapperPoxy是如何和Mapper.xml建立关联的,这个疑惑我们不妨也从SqlSession来入手,看看在盘古开天辟地的时候都发生了什么,不过这一些还是要从他的创建者SqlSessionFacotry说起了。
二、SqlSessionFactory的初始化
2.1 buildSqlSessionFactory
在Spring中SqlSessionFactory由SqlSessionFactoryBean的getObject()得到,我们来看下getObject():
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
再来看下afterPropertiesSet()方法,里面调用了buildSqlSessionFactory的buildSqlSessionFactory()。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
继续来看buildSqlSessionFactory(),方法代码比较长,我们先来阅读下文档注释
/**
* Build a {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance.
*
* The default implementation uses the standard MyBatis {@code XMLConfigBuilder} API to build a
* {@code SqlSessionFactory} instance based on a Reader. Since 1.3.0, it can be specified a {@link Configuration}
* instance directly(without config file).
*
* @return SqlSessionFactory
* @throws Exception
* if configuration is failed
*/
文档大意是该方法默认实现使用标准的MyBatis XMLConfigBuilder API去该方法用来构建SqlSessionFactory实例基于一个Reader。 从1.3.0版本以后,它可以指定Configuration实例不依赖配置文件。
2.2 构建Configuration
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(
() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach(plugin -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
});
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeHandlersPackage, TypeHandler.class).stream().filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface()).filter(clazz -> !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()))
.forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry()::register);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach(typeHandler -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
});
}
...
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
乍一看,有点懵逼,这个方法也太长了。我们先不看具体内容就看结构。好多if判断,条件都带this,是SqlSessionFactoryBean的属性字段。那么他们到底是什么意思呢?我们回到SqlSessionFactoryBean这个类上。看下他们的set方法原来调用他们的就是sqlSessionFactory()方法
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
applyConfiguration(factory);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
...
return factory.getObject();
this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation())果然和SpringBoot的配置文件有关系。 在看看typeAliasesPackage,mapperLocations这些属性字段,是不是有点眼熟?这不是引入Mybatis在.yml文件中mybatis的配置吗!我们来看下 官方文档的介绍:
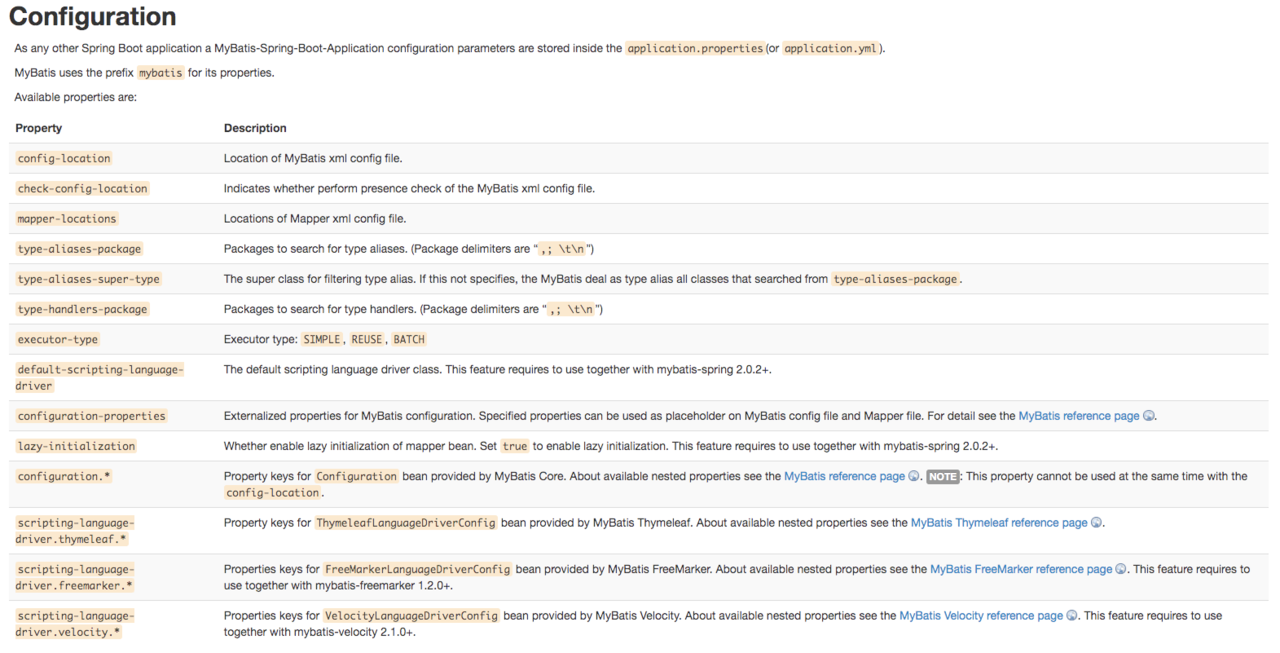
# application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.example.domain.model
mybatis.type-handlers-package=com.example.typehandler
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
mybatis.configuration.default-fetch-size=100
mybatis.configuration.default-statement-timeout=30
...
# application.yml
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.example.domain.model
type-handlers-package: com.example.typehandler
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
default-fetch-size: 100
default-statement-timeout: 30
...
三、MappedStatement是怎么来的?
这里咱们说一个比较重要的配置mapper-locations ,mapper-locations`我们通常会配置mapper类所在的相对路径,下面我们看下代码的处理:
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
}
- 构建XMLMapperBuilder对象
- 调用parse()进行解析
3.1 XMLMapperBuilder
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver()),
configuration, resource, sqlFragments);
}
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}
构建XMLMapperBuilder用到了inputStream(Mapper文件的输入流),Configuration和Resource(Mapper文件的路径). 来看下parse方法:
3.2 parse()
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 配置文件为第一次加载时才会执行完整的解析操作
// 读取并配置MapperXml文件的内容 核心逻辑
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 记录已加载当前的配置文件
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 绑定DAO操作接口和当前配置的关系
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 解析处理过程中因为异常未完成处理的ResultMap
parsePendingResultMaps();
// 解析处理过程中因为异常未完成处理的缓存引用
parsePendingCacheRefs();
// 解析处理过程中因为异常未完成处理的语句
parsePendingStatements();
}
parse主要了以下这些事情
- 读取并配置MapperXml文件的内容
- 记录已加载当前的配置文件
- 绑定DAO操作接口和当前配置的关系
- 补偿操作处理之前未完成的ResultMap缓存等
我们来看下configurationElement(),parse的核心逻辑。
3.2.1 configurationElement
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//解析mapper标签中的namespace
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
//解析缓存相关设置
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
//解析parameterMap
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
//解析resultMap
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
//解析引入的sql头
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//解析sql语句标签构建MapperStatement
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
这里的XNode context就是我们*Mapper.xml中<mapper>...</mapper>的内容了,解析的结果最终都会放在Configuration中,有兴趣的同学可以跟下代码了解下每一步是怎么解析的,这里就不过多描述了。我们重新来分析一下 buildStatementFromContext()方法看下是如何加载xml的sql内容的。
3.2.2 XMLStatementBuilder
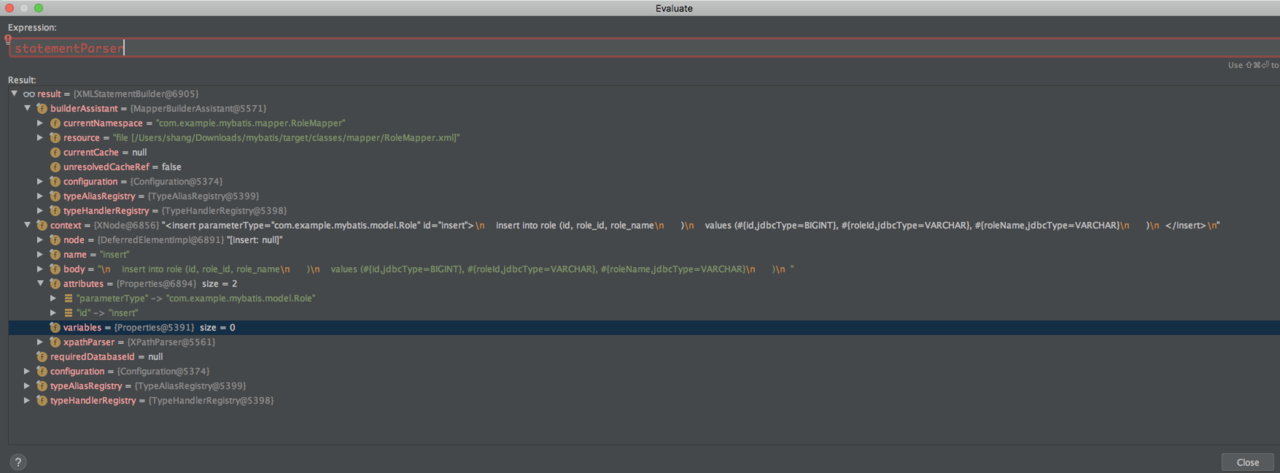
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
这里的list已经经过 context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete")解析。
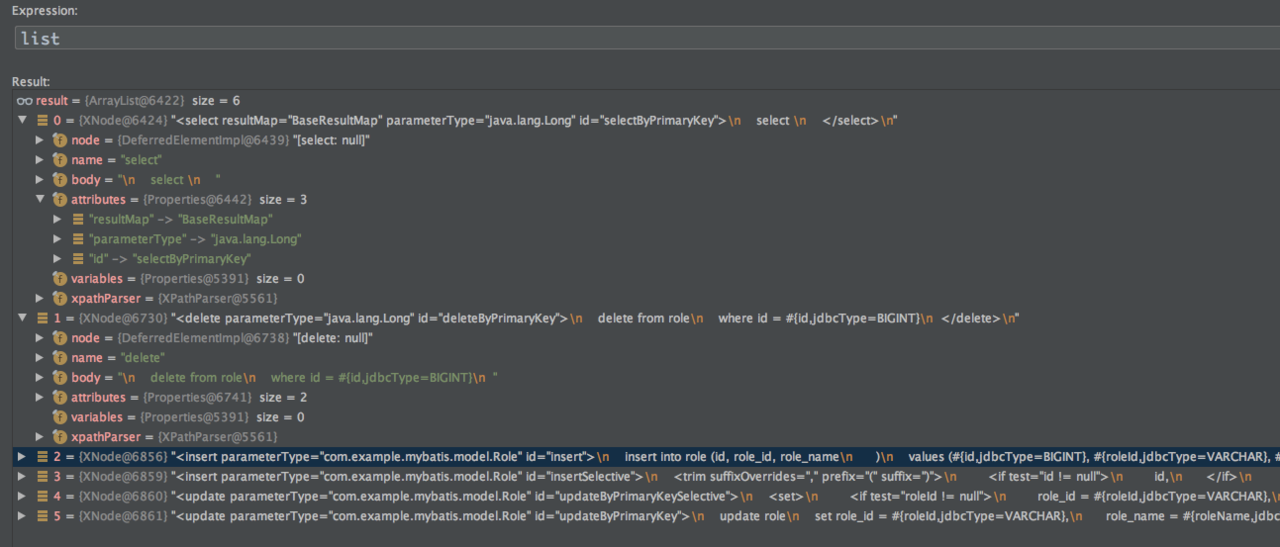
configuration, builderAssistant(namespace等信息), context(XNode), requiredDatabaseId(数据源id引用多数据源时会用到)构建一个 XMLStatementBuilder对象。
3.2.3 parseStatementNode
我们再来看一下parseStatementNode()方法,其实无非就是根据Attribute去拿数据,这里我需要关注SqlSource这个属性,它实际上就是我们解析出来的sql语句。
/**
* 完成指定Statement的解析操作
*/
public void parseStatementNode() {
// step1: 基础属性的取值操作
// 获取声明语句的唯一标志
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
// 获取对应的数据库唯一标志
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 校验数据库类型是否匹配
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 如果数据库类型不一致,跳过处理
return;
}
// 获取内容的大小限制
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
// 超时时间
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
// 参数映射
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
// 参数类型
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
// 解析参数类
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
// 响应映射
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
// 响应类型
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
// 语言类型
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
// 获取语言驱动
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// 解析响应类类型
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
// 解析不可重复响应集合
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
// 解析语句的声明类型,mybatis目前支持三种,prepare、硬编码、以及存储过程调用
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
// 解析响应集合类型
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
// 根据节点的名称获取SQL语句类型
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 判断是否为查询语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 是否刷新缓存,非查询语句(insert|update|delete)才会刷新缓存
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
// 是否应用缓存,查询语句(select)才会应用缓存
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
// 查询结果是否有序且成组
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// step2: 特殊元素的解析操作
// 解析内部的Include标签
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
// 解析并处理include标签
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// 解析select声明语句的selectKey内容
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 解析SQL内容
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// 获取select声明语句的resultSets属性声明
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
// 获取update声明语句的resultSets属性声明
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
// 获取insert声明语句的keyColumn属性声明
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
// 配置主键生成器
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
// 合并命名空间
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
// 获取主键生成器
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
// 已有直接获取
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
// 没有则生成
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
// step3: MappedStatement对象的构建工作
// 构建整体配置
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
最后通过 builderAssistant.addMappedStatement方法生成MappedStatement对象,并将其存储在Configuration中
3.2.4 addMappedStatement
...
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {
mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
这里的id可以通过代码得知:mapperInterface + methodName
public String applyCurrentNamespace(String base, boolean isReference) {
if (base == null) {
return null;
}
if (isReference) {
// is it qualified with any namespace yet?
if (base.contains(".")) {
return base;
}
} else {
// is it qualified with this namespace yet?
if (base.startsWith(currentNamespace + ".")) {
return base;
}
if (base.contains(".")) {
throw new BuilderException("Dots are not allowed in element names, please remove it from " + base);
}
}
return currentNamespace + "." + base;
}
3.3 bindMapperForNamespace
前面说到XMLMapperBuilder在parse()的时候,在读取并配置xml文件后,还有一个bindMapperForNamespace()的操作,用来绑定Mapper和xml文件的对应关系。
/**
* 绑定Mapper和命名空间的关系,这里的mapper代指DAO操作接口
*/
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 加载Mapper文件对应的Dao操作接口
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// 如果尚未绑定该资源则执行下列处理
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResourceloadXmlResource
// 注册已加载过的资源集合
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 注册DAO操作接口
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
这里addMapper()会初始化MapperProxy和MapperProxyFactory的map对象,同时在 parse()方法会处理@select等注解型的Mapper函数。这个之前我们说MapperPoxy初始化的时候有提到过,这里就不继续展开了。
四、 MapperPoxy和MapperStatement如何建立联系
在程序执行Mapper接口某个具体方法时,会调用MapperPoxy的invoke()方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
invoke()实际上是执行了MapperMethod类的execute()方法实现了和数据库的交互,我们先看下MapperMethod这个类:
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
SqlCommand:
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
//获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
在这里我们看到了MappedStatement,也就是之前解析*mapper.xml文件并放在Configuration中的sql信息。我们继续往下看resolveMappedStatement():
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
//接口名+方法名做id
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
//获取Configuration中的MappedStatement
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
看到mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;怎么样,很熟悉吧。没错这里就是通过接口名+方法名拿到了存在Configuration中的MappedStatement。 也就是说MapperPoxy在invoke的时候会去Configuration获取对应的的MappedStatement,他们是这样联系起来的。
五、总结
SqlSessionFacotry的初始化是通过SqlSessionFactoryBean的getObject()得到.SqlSessionFactoryBean在getObject()之前会读取Mybatis的相关配置到SqlSessionFactoryBean的属性中,调用getObject()的时候会将这些配置信息处理并放置在Configuration中,同时Configuration也是创建SqlSessionFactory的重要参数.mapper-locations这个配置项目是配置Mapper文件路径的,先构建XMLMapperBuilder对象,调用parse()进行解析.parse()主要了做了读取并配置MapperXml文件的内容、记录已加载当前的配置文件、绑定DAO操作接口和当前配置的关系、补偿操作处理之前未完成的ResultMap缓存等.- 在解析xml文件的sql标签时,会通过
addMappedStatement()生成MappedStatement对象,并将以mapperInterface + methodName为key,MappedStatement对象为vlaue以为map的形式存储在Configuration中. - 绑定Mapper和nameSpace对应对应关系时,会触发
configuration.addMapper()初始化MapperPoxy. - MapperPoxy在被
invoke的时候,会通过mapperInterface + methodName从Configuration中获取对应解析好的MappedStatement