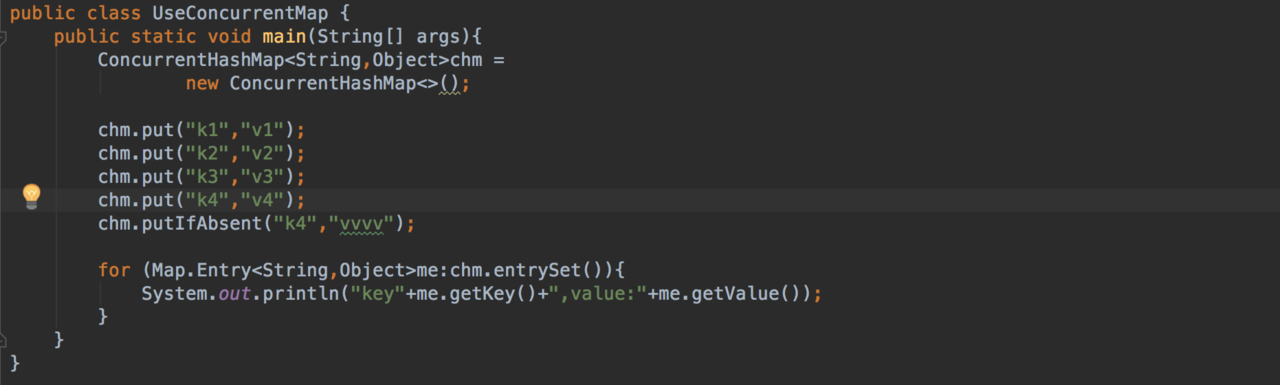
putIfAbsent 源代码
public V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null)
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, true);
}
put源代码
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
前面一段都是一样的,都是先计算hash再同步取值,区别在于最后一句
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
return s.put(key, hash, value, true);
putIfAbsent下不会进入修改e.value
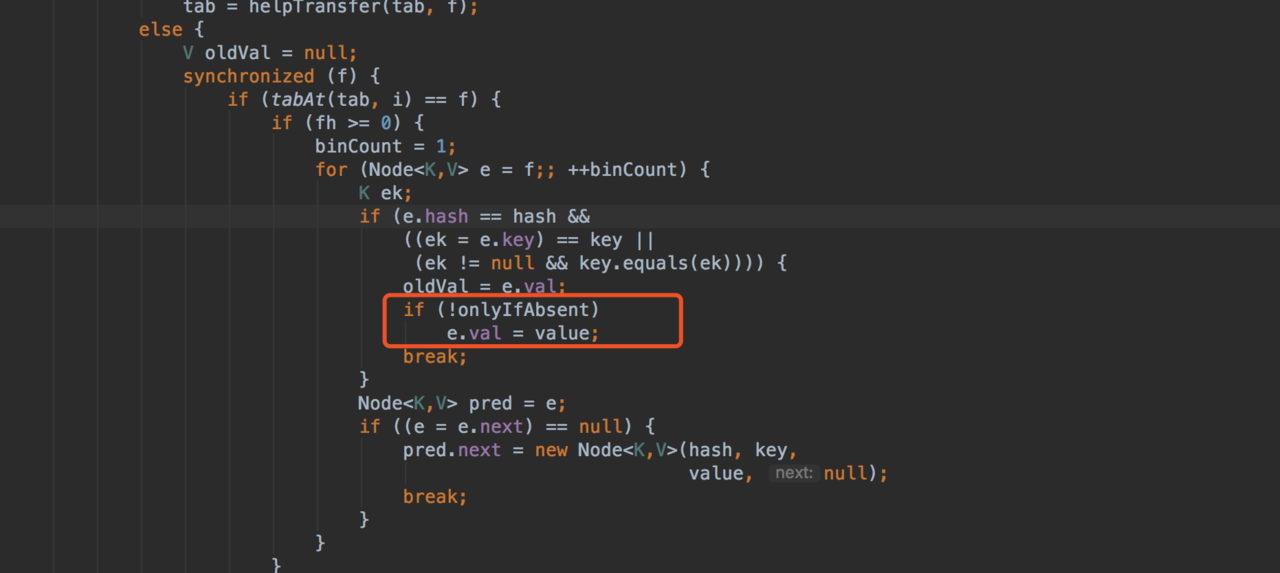
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
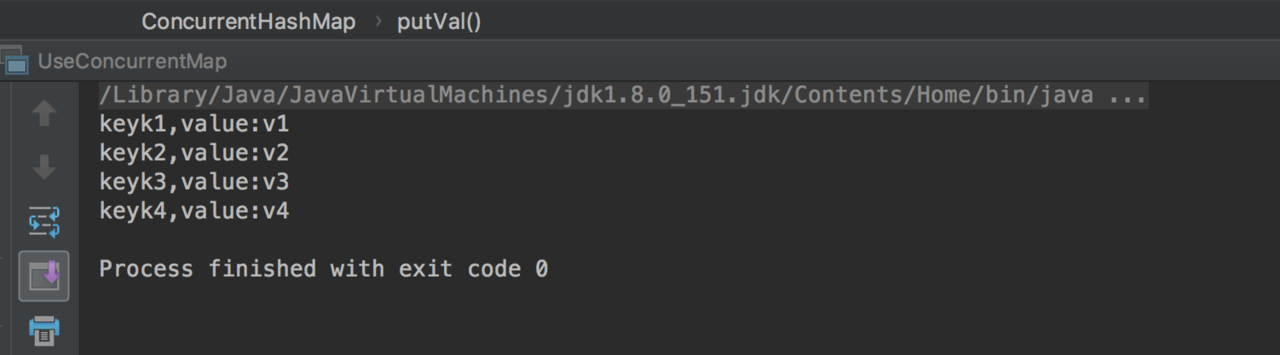
ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>();
System.out.println(map.put("userName", "1"));
System.out.println(map.put("userName", "2"));
System.out.println(map.get("1"));
打印出来是
2
putIfAbsent方法,则打印出来是1,
因此可以知道onlyIfAbsent,key存在的情况下,在putIfAbsent下不会修改,而put下则会修改成新的值